Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2023-2024
Date & Time: 19th March 2024, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully and follow them:
- This question paper contains 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper is divided into FIVE sections - Section A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A - question number 1 to 16 are multiple choice type questions. Each question carries 1 mark.
- Section B - question number 17 to 21 are very short answer type questions. Each question carries 2 marks.
- Section C - question number 22 to 28 are short answer type questions. Each question carries 3 marks.
- Section D - question number 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question carries 4 marks. Each question has subparts with internal choice in one of the subparts.
- Section E - question number 31 to 33 are long answer type questions. Each question carries 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in section B, C and D of question paper. A candidate has to write answer for only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Kindly note that there is a separate question paper for Visually Impaired candidates.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
In a fertilized ovule of an angiosperm, the cells in which n, 2n and 3n conditions respectively occur are ______.
Antipodal, zygote and endosperm
Zygote, nucellus and endosperm
Endosperm, nucellus and zygote
Antipodals, synergids and integuments
Chapter:
Study the following diagram of Transverse Section of a young anther of an angiosperm:
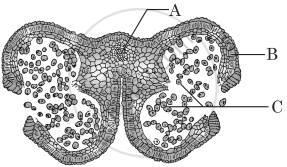
Select the option where parts ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ are correctly identified.
A – Connective, B – Endothecium, C – Pollen grain.
A – Endothecium, B – Connective, C – Pollen grain.
A – Pollen grain, B – Connective, C – Endothecium.
A – Endothecium, B – Pollen grain, C – Connective.
Chapter:
Identify the category of genetic disorder depicted in the pedigree chart given below:
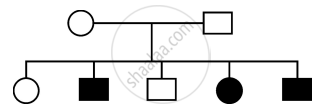
X-Linked recessive
X-Linked dominant
Autosomal recessive
Autosomal dominant
Chapter:
Which of the options has correct identification of ‘P’, ‘Q’ and ‘R’ in the illustration of ‘Central Dogma’ given below?
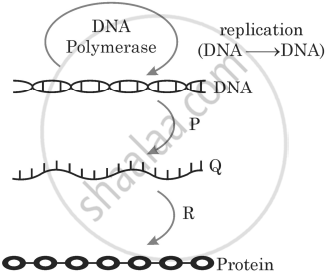
P – Replication, Q – rRNA, R – Transcription
P – Translation, Q – mRNA, R – Transcription
P – Replication, Q – mRNA, R – Translation
P – Transcription, Q – mRNA, R – Translation
Chapter:
Hugo de Vries proposed the mutation theory of organic evolution after his experiments on ______.
Garden pea
Evening primrose
Fruit fly
Four O’ clock plant
Chapter:
A list of organisms is given in column ‘R’, whereas in column ‘S’ a list of products produced by them:
| Column 'R' | Column 'S' | ||
| (Organisms) | (Products) | ||
| (A) | Lactobacillus | (i) | Cheese |
| (B) | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | (ii) | Curd |
| (C) | Aspergillus niger | (iii) | Citric acid |
| (D) | Acetobacter aceti | (iv) | Bread |
| (v) | Acetic acid |
Select the option where the organisms are correctly matched with the product.
(A) - (ii), (B) - (i), (C)- (iii), (D) - (v)
(A) - (ii), (B) - (iv), (C) - (v), (D) - (iii)
(A) - (ii), (B) - (iv), (C) - (iii), (D) - (v)
(A) - (iii), (B) - (iv), (C) - (v), (D) - (i)
Chapter:
Study the table given below:
| Contraceptive/Contraceptive Method | Mode of Action | ||
| A. | The pill | I. | Prevent sperm reaching cervix |
| B. | Condom | II. | Prevent implantation |
| C. | Vasectomy | III. | Inhibits ovulation |
| D. | Copper-T | IV. | Semen contains no sperm |
Select the option where contraceptive/contraceptive method are correctly matched with their mode of action.
A – III, B – II, C – I, D – IV
A – II, B – III, C – I, D – IV
A – III, B – I, C – IV, D – II
A – IV, B – III, C – II, D – I
Chapter:
Select the option that gives the correct identification of ovum, morula and blastocyst in a human female reproduction system, as shown in the following diagram:
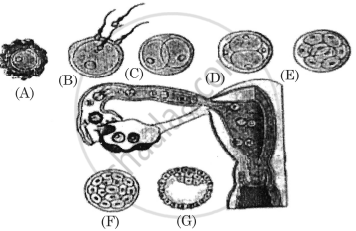
Ovum – B, Morula – D, Blastocyst – F
Ovum – A, Morula – B, Blastocyst – G
Ovum – A, Morula – E, Blastocyst – G
Ovum – B, Morula – D, Blastocyst – G
Chapter:
The commonly used vector for human genome sequencing was/were:
Retrovirus
T-DNA
BAC and YAC
Plasmid Vector
Chapter:
Turner’s syndrome in humans occurs due to
Aneuploidy
Euploidy
Polyploidy
Autosomal abnormality
Chapter:
ELISA technique is based on the principle of ______.
DNA replication
Antigen-antibody interaction
Pathogen–antigen interaction
Antigen–protein interaction
Chapter:
The ‘molecular scissors’ fall in the category of ______.
Cleaving enzyme
Endonuclease
Exonuclease
Restriction enzymes
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Plasmids are autonomously replicating circular extra-chromosomal DNA.
Reason (R): Plasmids are usually present in Eukaryotic cells.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): A given fig species can be pollinated only by its partner’ wasp.
Reason (R): The wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence while searching for suitable egg laying sites.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Some aquatic ecosystems have inverted biomass pyramids.
Reason (R): More energy is required by the organisms occupying higher trophic levels.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter:
Assertion (A): Patents are granted by government to an inventor.
Reason (R): Patents prevents others from commercial use of an invention.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter:
Explain the improvement in the quality of the milk produced by it.
Chapter:
Study the graph given below that represents the changes in the thickening of the uterine wall in women ‘X’ and women ‘Y’ over a period of one month:
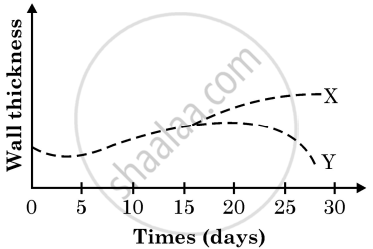
What does the graph with respect to woman ‘X’ and woman ‘Y’ indicate? Give suitable reason.
Chapter:
Mention any two ways by which HIV can be transmitted to a healthy person.
Chapter:
Mention any two ways by which Hepatitis-B can be transmitted to a healthy person.
Chapter:
Advertisements
Why is an early detection of HIV diseases essential?
Chapter:
Why is an early detection of hepatitis-B diseases essential?
Chapter:
Biodiversity hotspots cover less than 2% of Earth’s land area. Strict protection of these areas can reduce the rate of ongoing extinctions. Explain.
Chapter:
Name any two biodiversity hot spots in India.
Chapter: [0.13] Biodiversity and Its Conservation
Differentiate between grazing food chain and detritus food chain.
Chapter:
What is brood parasitism? Explain with the help of an example.
Chapter: [0.11] Organisms and Populations
Draw a schematic diagram of the E. coli vector pBR 322 and mark the following in it:
- ori
- rop
- ampicillin resistant gene
- tetracycline-resistant gene
- restriction site Bam HI
- restriction site EcoRI
Chapter:
How has the use of Agrobacterium as vector helped in controlling Meloidogyne incognita infestation in tobacco plants? Explain in correct sequence.
Chapter:
Explain the role of the flocs during the sewage treatment.
Chapter:
Explain the role of the anaerobic sludge digester during the sewage treatment.
Chapter:
Whose skulls ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’ are shown below? Which of the two are more similar to each other?

Chapter:
Name the ape-like primates that existed 1.5 million years ago.
Chapter:
Name the man-like primates that existed 1.5 million years ago.
Chapter:
- Name the group of drugs whose skeletal molecule is shown below: [1]
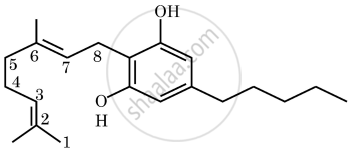
- How are such drugs consumed? [1]
- Name the human body organ affected by the consumption of these drugs. [1]
Chapter:
Draw a schematic diagram of an antibody molecule and label any 4 parts.
Chapter:
Mention the chemical nature of the antibody molecule.
Chapter:
Advertisements
Name the cells that produce antibody molecules.
Chapter:
A pea plant with purple flowers, when crossed with a plant with white, produced 50 plants with only purple flowers. On selfing these plants produced 482 plants with purple flower and 162 with white flowers. Explain the pattern of inheritance with the help of Punnet square.
Chapter:
Draw a well labelled diagram of sectional view of male gametophyte/microspore of an angiosperm and write the functions of any two parts labelled. (Any four labels).
Chapter:
Read the following passage:
| Generally, in eukaryotic cells the average length of a transcription unit along a DNA molecule is about 8,000 nucleotides, so the RNA product of the transcription is also that long. But it only takes about 1200 nucleotides from the above RNA product to translate average sized polypeptide of 400 Amino acids. |
- Name this RNA product transcribed from the DNA that subsequently translates into a polypeptide of 400 amino acids. Mention the enzyme responsible for transcribing this type of RNA from the DNA. [1]
- Name and explain the process the RNA molecule transcribed from 8000 nucleotide long DNA undergoes to be able to translate a polypeptide of 400 amino acids. [2]
- Write the number of RNA polymerases involved in the transcription of DNA in a prokaryote and eukaryotes. [1]
OR
Mention the difference in the site of transcription in a prokaryote and eukaryote cell. [1]
Chapter:
Read the following passage:
| Populations evolve to maximise their reproductive fitness in the habitat in which they live. Ecologists suggest, the life history of organisms have evolved in relations to the constraints imposed by the biotic and abiotic components of the habitat in which they live. This gets reflected in the population growth pattern of all organisms including humans. |
Study the population growth curves shown in the given graph and answer the questions that follow:
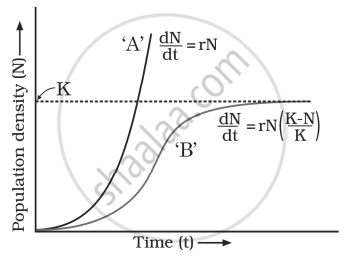
- Identify the growth curves ‘A’ and ‘B’. [1]
- Mention what does the dotted line in the graph indicate and state its importance also. [1]
OR
Growth curve ‘B’ shows a different pattern from that of growth curve ‘A’. Justify giving one reason. [1]
- Which one of the two curves is more “realistic” and why? [1]
- Which one of the two curves is relevant in present days with respect to human population in our country and why? [1]
Chapter:
Study the schematic diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
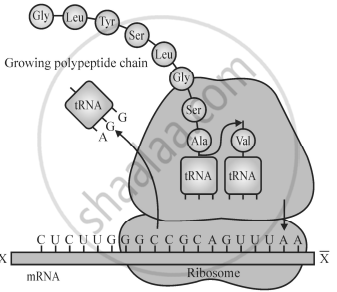
- Identify the polarity from 'X' to '`bar(X)`' in the mRNA segment shown. Mention how many more amino acids can be added to the polypeptide that is being translated and why. [1.5]
- Write the initiating codon for translation, its anticodon and the amino acid it codes for. [1.5]
- Explain the charging of an adaptor molecule. Why this molecule needs to be charged? [1]
Chapter:
Why is sickle-cell anaemia, a human blood disorder so named?
Chapter:
Explain the genetic basis that results in the expression of sickle-cell anaemia disorder.
Chapter:
Work out a cross to explain how normal parents may have a sickle-cell anaemic child.
Chapter:
Describe the life cycle of HIV from the time of its entry into the human body till full blown AIDS sets in.
Chapter:
Describe the different steps in the sexual mode of reproduction in the life cycle of a malarial parasite from the time of its initiation till where it is completed and ready to start a fresh cycle.
Chapter:
State the objective of adopting artificial hybridisation programme in plants.
Chapter:
Describe the steps followed in the artificial hybridisation program in plants technique.
Chapter:
Describe the development of placenta during pregnancy in a human female.
Chapter:
Explain the role of placenta development during pregnancy in a human female.
Chapter:
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Biology with solutions 2023 - 2024
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2024 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Biology, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Biology will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
