ISC (Commerce)
ISC (Arts)
ISC (Science)
Academic Year: 2012-2013
Date: मार्च 2013
Advertisements
Answer all questions in Part I and six questions from Part II, choosing two questions from Section A, two from Section B and two from Section C.
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets :
(zero, first, second, increased, decreased, anode, cathode, active, inactive, potassium cyanide, internal, external, dependent, independent, red, benzoic acid, benzoin, common ion effect, salt hydrolysis, alkali, potassium hydroxide,)
(i) In a galvanic cell, electrons flow from ………. to ……….. through the connecting wires.
(ii) Racemic mixtures are optical …………. because of …………… compensation.
(iii) The half-life period of a …………. order reaction is …………. of the concentration of the reactant.
(iv) Benzaldehyde when treated with an alcoholic solution of ……… forms ………..
(v) The solubility of calcium oxalate is …………. in the presence of ammonium oxalate because of ……… .
Chapter: [0.062] Galvanic cells, mechanism of current production in a galvanic cell;
The compound which is optically active is:
1-butanol
2-butanol
1-propanol
2-methyl-1-propanol
Chapter: [0.15] Cyanides, Isocyanides, Nitro compounds, Amines and Diazonium Salt
The salt which will not hydrolyse in aqueous solution is:
Copper sulphate
Sodium sulphate
Potassium cyanide
Sodium carbonate
Chapter: [0.053] Salt hydrolysis
Copper has the face centred cubic structure. The coordination number of each ion is:
4
12
14
8
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
For the reaction 2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3, the unit of an equilibrium constant is :
L mol-1
J mol-1
mol L-1
[L mol-1]2
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Reversible reactions and dynamic equilibrium
The deficiency of vitamin D causes:
Rickets
Gout
Scurvy
Night blindness.
Chapter: [0.17] Biomolecules – carbohydrates, proteins, enzymes, vitamins and nucleic acids
Two metallic elements A and B have the following standard oxidation potentials: A = 0·40v B = - 0·80v. What would you expect if element A was added to an aqueous salt solution of element B? Give a reason for your answer.
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
Two moles of NH3 are introduced into the one-litre flask in which it dissociates at high temperature as follows: 2NH3(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 3H2(g). Determine Kc, if at equilibrium 1 mole of NH3 remains.
Chapter: [0.0301] Order of a reaction
Give a balanced equation for the preparation of salicylaldehyde from phenol.
Chapter: [0.121] Methods of preparation, manufacture, properties and use
If the half-life period for a first-order reaction is 69-3 seconds, what is the value of its rate constant?
Chapter: [0.0301] Order of a reaction
Define cryoscopic constant.
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Relative molecular mass of non-volatile substances
Match the following:
| (i) | Colligative property | (a) | Polysaccharide |
| (ii) | Nicol prism | (b) | Osmotic pressure |
| (iii) | Activation energy | (c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | Starch | (d) | Polarimeter |
| (v) | Acetaldehyde | (e) | Arrhenius equation |
Chapter: [0.011000000000000001] Raoult's law and colligative properties
Ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze agent. Calculate the amount of ethylene glycol to be added to 4 kg of water to prevent it from freezing at -6°C. (Kf for H2O = 1 .85 K mole-1 kg)
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Relative molecular mass of non-volatile substances
The freezing point of a solution containing 0·3gms of acetic acid in 30gms of benzene is lowered by 0.45K. Calculate the Van't Hoff factor. (at. wt. of C = 12, H = 1, O = 16, Kf for benzene = 5· 12K kg mole-1).
Chapter: [0.013000000000000001] Relative molecular mass of non-volatile substances
When water is added to 0.01M aqueous solution of acetic acid the number of hydrogen ions increases.
Chapter: [0.055999999999999994] Ostwald’s dilution law and its derivation
When 96500 coulombs of electricity is passed through acidulated water, 5·6 litres of oxygen at s.t.p. is liberated at the anode.
Chapter: [0.061] Faraday’s laws of Electrolysis, Coulometer
Advertisements
Arrange Ag, Cr and Hg metals in the increasing order of reducing power. Given:
`(E_(Ag^+)^o)/(Ag) = +0.80V`
`(E_(Cr^(+3))^o)/(Cr) = -0.74V`
`(E_(Hg^(+2))^o)/(Hg) = +0.79V`
Chapter: [0.062] Galvanic cells, mechanism of current production in a galvanic cell;
In a first-order reaction, 10% of the reactant is consumed in 25 minutes Calculate:
(i) The half-life of the reaction.
(ii) The time required for completing 17% of the reaction.
Chapter: [0.0301] Order of a reaction
A solution of NH4Cl and NH4OH acts as a buffer.
Chapter: [0.054000000000000006] Buffer solutions
Cu is precipitated as CuS while Zn is not precipitated when H2S is passed through an acidic solution of Cu(NO3 )2 and Zn(NO3)2 respectively.
Chapter: [0.054000000000000006] Buffer solutions
What is Schottky defect in a solid?
Chapter: [0.02] States of Matters: Structure and Properties Solid State
A bcc element (atomic mass 65) has a cell edge of 420 pm. Calculate its density in gms/cm3 .
Chapter: [0.02] States of Matters: Structure and Properties Solid State
The rate of the reaction`H_2 +I_2 ⇌ 2HI` is given by:
Rate = 1.7 × 10-19 [H2] [I2] at 25°C.
The rate of decomposition of gaseous HI to H2 and I2 is given by:
Rate = 2.4 × 10-21 [HI]2 at 25°C.
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the formation of HI from H2 and I2 at 25°C.
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Reversible reactions and dynamic equilibrium
Give Lewis's definition of acids and bases.
Chapter: [0.051] Arrhenius, Brönsted-Lowry and Lewis concept of acids and bases
The solubility of Ag2CrO4 at 25°C is 8.0 × 10-5 moles litre-1. Calculate its solubility product.
Chapter: [0.055] Solubility product and its applications
Define the molar conductance of a solution. State its unit. How is it related to the specific conductance of a solution?
Chapter: [0.064] Electrolytic conductance
Calculate the value of Ecell at 298 K for the following cell:
`(Al)/(Al^(3+)) (0.01M) || Sn^(2+) ((0.015 M))/(Sn)`
`E° _(Al^(3+))/(AI)= -1.66 " Volt and " E° _(Sn^(2+)) /(Sn) = -0.14` volt
Chapter: [0.062] Galvanic cells, mechanism of current production in a galvanic cell;
Calculate the degree of hydrolysis of 0.2 (M) sodium acetate solution.
(Hydrolysis constant of sodium acetate = 5.6 × 10-10 and ionic product of H2O = 10-14 at 25°C).
Chapter: [0.057] Common ion effect
Explain why high pressure is used in the manufacture of ammonia by Haber's process. Stiite the law or principle used.
Chapter: [0.040999999999999995] Reversible reactions and dynamic equilibrium
Give the IUPAC names of the following coordination compounds:
(i) K2[Zn(OH)4]
(ii) [CO(NH3)5 (CO3)] Cl.
Chapter: [0.07] Coordination Compounds
Advertisements
For the complex ion [Fe (CN)6]3- state:
(i) The geometry of the ion.
(ii) The magnetic property of the ion.
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
What type of structural isomers are [Co(NH3)5 Br] SO4 and [Co(NH3)5 SO4]Br? Give a chemical test to distinguish the isomers.
Chapter: [0.07] Coordination Compounds
For the molecule XeF2 :
(i) Draw the structure of the molecule indicating the lone pairs.
(ii) State the hybridization of the central atom.
(iii) State the ge.ometry of the molecule.
Chapter: [0.08] Chemistry of p-Block Elements: Group 16, 17, 18
Give balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
(i) Fluorine treated with a dilute sodium hydroxide solution.
(ii) Hydrogen sulphide treated with concentrated sulphuric acid.
(iii) Potassium iodide treated with acidified potassium pennanganate solution.
Chapter: [0.08] Chemistry of p-Block Elements: Group 16, 17, 18
In the extraction of zinc from zinc blende:
(i) Give an equation to show how zinc oxide is converted to zinc.
(ii) How is impure zinc finally electro-refined?
Chapter: [0.1] Chemistry of Transition and Inner-Transition Elements: d-Block: 3d, 4d and 5d series f-Block: 4f and 5f series
Explain why:
(i) Transition elements form coloured compounds.
(ii) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than their constituent elements.
(iii) Cu+ is diamagnetic but Cu2+ is paramagnetic. (Z = 29)
Chapter: [0.02] States of Matters: Structure and Properties Solid State
Nitrobenzene to benzene diazonium chloride.
Chapter: [0.15] Cyanides, Isocyanides, Nitro compounds, Amines and Diazonium Salt
Propanoic acid to ethylamine.
Chapter: [0.124] Classification, general formulae, structure and nomenclature [0.132] Ethers
Benzoic acid to benzaldehyde.
Chapter: [0.141] Carboxylic acids
Identify the compounds A, B, C, D, E and F:
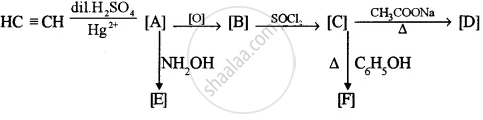
Chapter: [0.131] Carbonyl compounds
Acetamide is heated with bromine and sodium hydroxide solution.
Chapter: [0.142] Acid derivatives
Benzaldehyde is treated with 50% sodium hydroxide solution.
Chapter: [0.131] Carbonyl compounds
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds: Acetone and phenol.
Chapter: [0.12300000000000001] Distinction between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds: Formic acid and acetic acid.
Chapter: [0.141] Carboxylic acids
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pairs of compound:
(1) (C2H5)2NH and CH3-NH-C3H7
(2) 1 – butanol and 2 methyl-1 -propanol.
Chapter: [0.07] Coordination Compounds
Name the type of isomerism that the compound with molecular formula C3H6O2 exhibits. Represent the isomers.
Chapter: [0.07] Coordination Compounds
Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions:
Oxalic acid is treated with acidified potassium permanganate solution.
Chapter: [0.141] Carboxylic acids
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
Benzoic acid is treated with a mixture of concentrated nitric acid and concentrated sulphuric acid.
Chapter: [0.141] Carboxylic acids
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
Methyl magnesium iodide is treated with carbon dioxide and the product hydrolysed in acidic medium.
Chapter: [0.142] Acid derivatives
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reaction:
Ethylacetate is treated with ammonia.
Chapter: [0.142] Acid derivatives
An organic compound [A] having molecular formula C2H7N on treatment with nitrous acid gives a compound [B] having molecular formula C2H6O. [B] on treatment with an organic compound [C] gives a carboxylic acid [D] and a sweet-smelling compound [E]. Oxidation of [B] with acidified potassium dichromate also gives [D].
(i) Identify [A], [B], [C], [D] and [E].
(ii) Write a balanced chemical equation of [D] with chlorine in the presence of red phosphorus and name the reaction.
Chapter: [0.15] Cyanides, Isocyanides, Nitro compounds, Amines and Diazonium Salt
Acetamide is amphoteric in nature. Give two equations to support this statement.
Chapter: [0.142] Acid derivatives
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry (Theory) with solutions 2012 - 2013
Previous year Question paper for CISCE Class 12 -2013 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry (Theory), you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE Class 12.
How CISCE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry (Theory) will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
