Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Ionic Equilibria
4: Chemical Thermodynamics
5: Electrochemistry
6: Chemical Kinetics
7: Elements of Groups 16, 17 and 18
8: Transition and Inner transition Elements
9: Coordination Compounds
10: Halogen Derivatives
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Introduction to Polymer Chemistry
16: Green Chemistry and Nanochemistry
![Balbharati solutions for Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 1 - Solid State Balbharati solutions for Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 1 - Solid State - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-12-standard-hsc_6:74400b801d4c44ef8e058ff9d9dfe964.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Solid State
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of Maharashtra State Board Balbharati for Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC.
Balbharati solutions for Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC 1 Solid State Exercises [Pages 25 - 27]
Choose the most correct answer.
Molecular solids are ______.
crystalline solids
amorphous solids
ionic solids
metallic solids
Choose the most correct answer.
Which of the following is n-type semiconductor?
Pure Si
Si doped with As
Si doped with Ga
Ge doped with In
Choose the most correct answer.
In Frenkel defect, _______.
electrical neutrality of the substance is changed
density of the substance is changed
both cation and anion are missing
overall electrical neutrality is preserved
Choose the most correct answer.
In crystal lattice formed by bcc unit cell, the void volume is _______.
68%
74%
32%
26%
Choose the most correct answer.
The coordination number of atoms in bcc crystal lattice is _______.
2
4
6
8
Which of the following is not correct?
Four spheres are involved in the formation of a tetrahedral void.
The centres of spheres in octahedral voids are at the apices of a regular tetrahedron.
If the number of atoms is N, the number of octahedral voids is 2N.
If the number of atoms is N/2, the number of tetrahedral voids is N.
Choose the most correct answer.
A compound forms hcp structure. Number of octahedral and tetrahedral voids in 0.5 mole of substance is respectively _______.
3.011 × 1023, 6.022 × 1023
6.022 × 1023, 3.011 × 1023
4.011 × 1023, 2.011 × 1023
6.011 × 1023, 12.022 × 1023
Pb has fcc structure with edge length of unit cell 495 pm. Radius of Pb atom is ______.
205 pm
185 pm
260 pm
175 pm
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
What are the types of particles in each of the four main classes of crystalline solids?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Which of the three types of packing used by metals makes the most efficient use of space and which makes the least efficient use?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
The following pictures show population of bands for materials having different electrical properties. Classify them as insulator, semiconductor or metal.
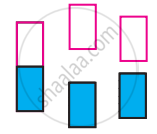
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
What is the unit cell?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
How does the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor change with temperature? Why?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
The picture represents bands of MOs for Si. Label valence band, conduction band, and band gap.
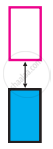
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
A solid is hard, brittle and electrically nonconductor. Its melt conducts electricity. What type of solid is it?
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Mention two properties that are common to both hcp and ccp lattices.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Sketch a tetrahedral void.
Answer the following in one or two sentences.
What are ferromagnetic substances?
Answer the following in brief.
What are valence band and conduction band?
Answer the following in brief.
Distinguish between ionic solids and molecular solids
Answer the following in brief.
Calculate the number of atoms in fcc unit cell.
Answer the following in brief.
How are the spheres arranged in first layer of simple cubic close-packed structures? How are the successive layers of spheres placed above this layer?
Answer the following in brief.
Calculate the packing efficiency of metal crystal that has simple cubic structure.
Answer the following in brief.
What are paramagnetic substances? Give examples.
What are the consequences of Schottky defect?
Answer the following in brief.
Cesium chloride crystallizes in a cubic unit cell with Cl– ions at the corners and a Cs+ ion in the center of the cube. How many CsCl molecules are there in the unit cell?
Cu crystallizes in fcc unit cell with edge length of 495 pm. What is the radius of Cu atom?
Obtain the relationship between the density of a substance and the edge length of the unit cell.
The density of iridium is 22.4 g/cm3. The unit cell of iridium is fcc. Calculate the radius of iridium atom. Molar mass of iridium is 192.2 g/mol.
Aluminium crystallizes in a cubic close-packed structure with a unit cell edge length of 353.6 pm. What is the radius of Al atom? How many unit cells are there in 1.00 cm3 of Al?
In ionic crystalline solid atoms of element Y form hcp lattice. The atoms of element X occupy one-third of tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound?
How are tetrahedral and octahedral voids formed?
Third layer of spheres is added to second layer so as to form hcp or ccp structure. What is the difference between the addition of third layer to form these hexagonal close-packed structures?
An element with molar mass 27 g/mol forms a cubic unit cell with edge length of 405 pm. If the density of the element is 2.7 g/cm3, what is the nature of the cubic unit cell?
An element has a bcc structure with a unit cell edge length of 288 pm. How many unit cells and a number of atoms are present in 200 g of the element? (1.16 × 1024, 2.32 × 1024)
Distinguish with the help of diagrams metal conductors, insulators and semiconductors from each other.
What are n-type semiconductors? Why is the conductivity of doped n-type semiconductor higher than that of pure semiconductor? Explain with diagram.
Explain with diagram, Frenkel defect. What are the conditions for its formation? What is its effect on density and electrical neutrality of the crystal?
What is an impurity defect? What are its types? Explain the formation of vacancies through aliovalent impurity with example.
Solutions for 1: Solid State
![Balbharati solutions for Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 1 - Solid State Balbharati solutions for Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 1 - Solid State - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-12-standard-hsc_6:74400b801d4c44ef8e058ff9d9dfe964.jpg)
Balbharati solutions for Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 1 - Solid State
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Balbharati solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board 1 (Solid State) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Balbharati textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 1 Solid State are Solid State, Types of Solids, Classification of Crystalline Solids, Crystal Structure, Cubic System, Packing of Particles in Crystal Lattice, Packing Efficiency, Crystal Defects or Imperfections, Electrical Properties of Solids, Magnetic Properties of Solids.
Using Balbharati Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC solutions Solid State exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Balbharati Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC students prefer Balbharati Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Solid State Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
