Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Is Matter Around Us Pure
3: Atoms and Molecules
4: Structure of the Atom
5: The Fundamental Unit of Life
6: Tissues
7: Diversity In Living Organisms
8: Motion
▶ 9: Force and Laws of Motion
10: Gravitation
11: Work and Energy
12: Sound
13: Why Do We Fall Ill
14: Natural Resources
15: Improvement In Food Resources
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Force and Laws of Motion NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Force and Laws of Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Force and Laws of Motion
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Science [English] Class 9.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 9 Force and Laws of Motion Multiple Choice Questions [Pages 61 - 62]
Which of the following statement is not correct for an object moving along a straight path in an accelerated motion?
Its speed keeps changing
Its velocity always changes
It always goes away from the earth
A force is always acting on it
According to the third law of motion, action and reaction
always act on the same body
always act on different bodies in opposite directions
have the same magnitude and directions
act on either body at normal to each other
A goalkeeper in a game of football pulls his hands backwards after holding the ball shot at the goal. This enables the goalkeeper to
exert larger force on the ball
reduce the force exerted by the ball on hands
increase the rate of change of momentum
decrease the rate of change of momentum
The inertia of an object tends to cause an object :
to increase its speed
to decrease its speed
to resist a change in its state of motion
to decelerate due to friction
A passenger in a moving train tosses a coin which falls behind him. This shows that the motion of train is :
accelerated
uniform
retarded
along circular track
An object of mass 2 kg is sliding with a constant velocity of 4 m/s on a frictionless horizontal table. The force required to keep this object moving with the same velocity is :
32 N
0 N
2 N
8 N
Rocket works on the principle of conservation of
mass
energy
momentum
velocity
A water tanker filled up to `2/3` of its tank with water is running at a uniform speed. When the brakes are suddenly applied, the water in its tank would
move backward
move forward
rise upwards
remain unaffected
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 9 Force and Laws of Motion Short Answer Questions [Pages 62 - 63]
There are three solids made up of aluminium, steel and wood, of the same shape and same volume. Which of them would have the highest inertia?
Two balls of the same size but of different materials, rubber and iron are kept on the smooth floor of a moving train. The brakes are applied suddenly to stop the train. Will the balls start rolling? If so, in which direction? Will they move at the same speed? Give reasons for your answer.
Two identical bullets are fired one by a light rifle and another by a heavy rifle with the same force. Which rifle will hurt the shoulder more and why?
A horse continues to apply force in order to move a cart with a constant speed. Explain why?
Suppose a ball of mass m is thrown vertically upward with an initial speed v, its speed decreases continuously till it becomes zero. Thereafter, the ball begins to fall downward and attains the speed v again before striking the ground. It implies that the magnitude of the initial and final momentums of the ball are the same. Yet, it is not an example of conservation of momentum. Explain why?
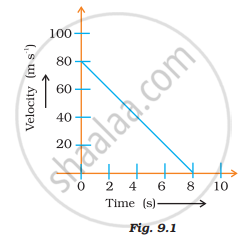
Velocity versus time graph of a ball of mass 50 g rolling on a concrete floor is shown in Fig. 9.1. Calculate the acceleration and frictional force of the floor on the ball.
A truck of mass M is moved under a force F. If the truck is then loaded with an object equal to the mass of the truck and the driving force is halved, then how does the acceleration change?
Two friends on roller-skates are standing 5 m apart facing each other. One of them throws a ball of 2 kg towards the other, who catches it, How will this activity affect the position of the two? Explain your answer.
The water sprinkler used for grass lawns begins to rotate as soon as the water is supplied. Explain the principle on which it works.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 9 Force and Laws of Motion Long Answer Questions [Page 63]
Using the second law of motion, derive the relation between force and acceleration. A bullet of 10 g strikes a sand-bag at a speed of 103 m s-1 and gets embedded after travelling 5 cm. Calculate
(i) the resistive force exerted by the sand on the bullet
(ii) the time is taken by the bullet to come to rest.
Derive the unit of force using the second law of motion. A force of 5N produces an acceleration of 8 m s–2 on a mass m1 and an acceleration of 24 m s–2 on a mass m2. What acceleration would the same force provide if both the masses are tied together?
What is momentum? Write its SI unit. Interpret force in terms of momentum. Represent the following graphically
(a) momentum versus velocity when mass is fixed.
(b) momentum versus mass when velocity is constant.
Solutions for 9: Force and Laws of Motion
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Force and Laws of Motion NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Force and Laws of Motion - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-9_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Science [English] Class 9 chapter 9 - Force and Laws of Motion
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE 9 (Force and Laws of Motion) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 9 chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion are Force, Force - Push or Pull, Effect of Force, Types of Force: Contact Force, Types of Force: Non-Contact Force, Balanced and Unbalanced Forces, Newton's First Law of Motion, Inertia and Mass, Newton's Second Law of Motion, Newton's Third Law of Motion, Conservation of Momentum, Force and Laws of Motion (Numerical).
Using NCERT Exemplar Science [English] Class 9 solutions Force and Laws of Motion exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 9 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Force and Laws of Motion Science [English] Class 9 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 9 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
