Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Nutrition in Animals
3: Heat
4: Acids, Bases and Salts
5: Physical and Chemical Changes
6: Respiration in Organisms
7: Transportation in Animals and Plants
8: Reproduction in Plants
▶ 9: Motion and Time
10: Electric Current and Its Effects
11: Light
12: Forests: Our Lifeline
13: Wastewater Story
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 7 chapter 9 - Motion and Time NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 7 chapter 9 - Motion and Time - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-7_6:325736d0fe154a27901a6745284d30d9.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 9: Motion and Time
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 9 of CBSE NCERT for Science [English] Class 7.
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 7 9 Motion and Time Exercises [Pages 105 - 106]
Classify the following motion:
Motion of your hands while running.
Straight line motion
Circular motion
Oscillatory motion
Classify the following motion:
Motion of a horse pulling a cart on a straight road.
Straight line motion
Circular motion
Oscillatory motion
Classify the following motion:
Motion of a child in a merry-go-round.
Straight line motion
Circular motion
Oscillatory motion
Classify the following motion:
Motion of a child on a see-saw.
Straight line motion
Circular motion
Oscillatory motion
Classify the following motion:
Motion of the hammer of an electric bell.
Straight line motion
Circular motion
Oscillatory motion
Classify the following motion:
Motion of a train on a straight bridge.
Straight line motion
Circular motion
Oscillatory motion
Which of the following are not correct?
The basic unit of time is second.
True
False
Every object moves with a constant speed.
True
False
Distances between two cities are measured in kilometres.
True
False
The time period of a given pendulum is constant.
True
False
The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
True
False
A simple pendulum takes 32 s to complete 20 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
The distance between two stations is 240 km. A train takes 4 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
The odometer of a car reads 57321.0 km when the clock shows the time 08:30 AM. What is the distance moved by the car, if at 08:50 AM, the odometer reading has changed to 57336.0 km? Calculate the speed of the car in km/min during this time. Express the speed in km/h also.
Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
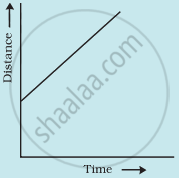
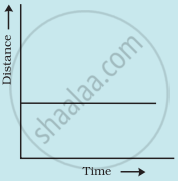
Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following case:
A car moving with a constant speed.
Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following case:
A car parked on a side road.
Which of the following relations is correct?
Speed = Distance × Time
Speed = `"Distance"/"Time"`
Speed = `"Time"/"Distance"`
Speed = `1/"Distance × Time"`
The basic unit of speed is ______.
km/min
m/min
km/h
m/s
A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is ______.
100 km
25 km
15 km
10 km
Suppose the two photographs, shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, had been taken at an interval of 10 seconds. If a distance of 100 metres is shown by 1 cm in these photographs, calculate the speed of the fastest car.
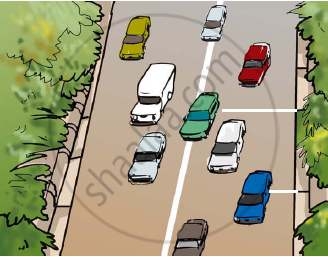
Figure 1 Vehicles moving in the same direction on a road
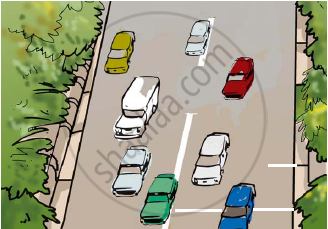
Figure 2 Position of vehicles shown in Figure 1 after some time
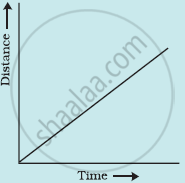
Figure shows the distance-time graph for the motion of two vehicles A and B. Which one of them is moving faster?
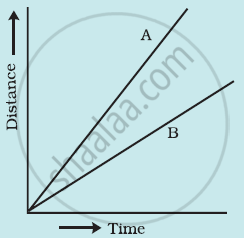
Figure: Distance-time graph for the motion of two cars
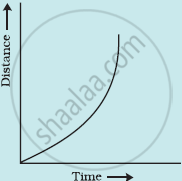
Which of the following distance-time graphs shows a truck moving with speed which is not constant?
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 7 9 Motion and Time Activities and Projects [Pages 107 - 108]
Extend Learning — Activities and Projects
You can make your own sundial and use it to mark the time of the day at your place. First of all, find the latitude of your city with the help of an atlas. Cut out a triangular piece of cardboard such that its one angle is equal to the latitude of your place and the angle opposite to it is a right angle. Fix this piece, called gnomon, vertically along a diameter of a circular board a shown in Figure One way to fix the gnomon could be to make a groove along a diameter on the circular board.
Next, select an open space, which receives sunlight for most of the day. Mark a line on the ground along the North-South direction. Place the sundial in the sun as shown in Figure Mark the position of the tip of the shadow of the gnomon on the circular board as early in the day as possible, say 8:00 AM. Mark the position of the tip of the shadow every hour throughout the day. Draw lines to connect each point marked by you with the centre of the base of the gnomon as shown in Figure Extend the lines on the circular board up to its periphery. You can use this sundial to read the time of the day at your place. Remember that the gnomon should always be placed in the North-South direction as shown in Figure.

Collect information about time-measuring devices that were used in the ancient times in different parts of the world. Prepare a brief write up on each one of them. The write up may include the name of the device, the place of its origin, the period when it was used, the unit in which the time was measured by it and a drawing or a photograph of the device, if available.
Make a model of a sand clock which can measure a time interval of 2 minutes.
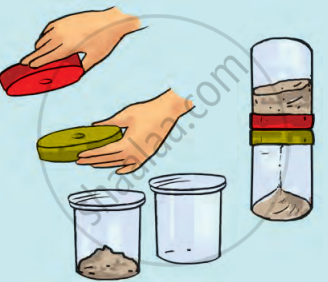
You can perform an interesting activity when you visit a park to ride a swing. You will require a watch. Make the swing oscillate without anyone sitting on it. Find its time period in the same way as you did for the pendulum. Make sure that there are no jerks in the motion of the swing. Ask one of your friends to sit on the swing. Push it once and let it swing naturally. Again measure its time period. Repeat the activity with different persons sitting on the swing. Compare the time period of the swing measured in different cases. What conclusions do you draw from this activity?
Solutions for 9: Motion and Time
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 7 chapter 9 - Motion and Time NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 7 chapter 9 - Motion and Time - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-english-class-7_6:325736d0fe154a27901a6745284d30d9.jpg)
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 7 chapter 9 - Motion and Time
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Science [English] Class 7 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 7 CBSE 9 (Motion and Time) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 7 chapter 9 Motion and Time are Measurement of Time, Devices for Measuring Time, Simple Pendulum for Time, Speed, Types of Speed, A Time Period of Oscillation and Frequency, Measuring Speed, Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph, Motion and Rest, Types of Motion, Measurement of Time, Devices for Measuring Time, Simple Pendulum for Time, Speed, Types of Speed, A Time Period of Oscillation and Frequency, Measuring Speed, Displacement - Time Graph Or Distance - Time Graph, Motion and Rest, Types of Motion.
Using NCERT Science [English] Class 7 solutions Motion and Time exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Science [English] Class 7 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 9, Motion and Time Science [English] Class 7 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 7 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.