Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 4 - Work, Energy and Power Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 4 - Work, Energy and Power - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Work, Energy and Power
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board 4 Work, Energy and Power Evaluation [Pages 203 - 206]
Multiple Choice Questions
A uniform force of `(2hati + hatj)` N acts on a particle of mass 1 kg. The particle displaces from position `(3hatj + hatk)` m to `(5hati + 3hatj)` m. The work done by the force on the particle is ______
9 J
6 J
10 J
12 J
A ball of mass 1 kg and another of mass 2 kg are dropped from a tall building whose height is 80 m. After, a fall of 40 m each towards Earth, their respective kinetic energies will be in the ratio of ______
`sqrt2` : 1
1 : `sqrt2`
2 : 1
1 : 2
A body of mass 1 kg is thrown upwards with a velocity of 20 ms−1. It momentarily comes to rest after attaining a height of 18 m. How much energy is lost due to air friction?.
20 J
30 J
40 J
10 J
An engine pumps water continuously through a hose. Water leaves the hose with a velocity v and m is the mass per unit length of the water of the jet. What is the rate at which kinetic energy is imparted to water?.
`1/2mv^3`
mv3
`3/2mv^2`
`5/2mv^2`
A body of mass 4 m is lying in xy-plane at rest. It suddenly explodes into three pieces. Two pieces each of mass m move perpendicular to each other with equal speed v. The total kinetic energy generated due to explosion is ______
`mv^2`
`3/2mv^2`
`2mv^2`
`4mv^2`
The potential energy of a system increases, if work is done ______
by the system against a conservative force
by the system against a nonconservative force
upon the system by a conservative force
upon the system by a nonconservative force
What is the minimum velocity with which a body of mass m must enter a vertical loop of radius R so that it can complete the loop?.
`sqrt(2gR)`
`sqrt(3gR)`
`sqrt(5gR)`
`sqrt(gR)`
The work done by the conservative force for a closed path is ______
always negative
zero
always positive
not defined
If the linear momentum of the object is increased by 0.1%, then the kinetic energy is increased by ______
0.1 %
0.2%
0.4%
0.01%
If the potential energy of the particle is `α - β/2x^2`, then the force experienced by the particle is ______
`F = beta/2x^2`
F = βx
F = -βx
`F = -beta/2x^2`
A wind-powered generator converts wind energy into electric energy. Assume that the generator converts a fixed fraction of the wind energy intercepted by its blades into electrical energy. For wind speed v, the electrical power output will be proportional to ______
v
v2
v3
v4
Two equal masses m1 and m2 are moving along the same straight line with velocities 5 ms-1 and -9 ms-1 respectively. If the collision is elastic, then calculate the velocities after the collision of m1 and m2, respectively.
-4 ms-1 and 10 ms-1
10 ms-1 and 0 ms-1
-9 ms-1 and 5 ms-1
5 ms-1 and 1 ms-1
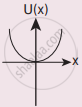
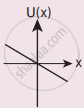
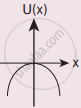
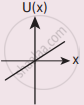
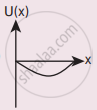
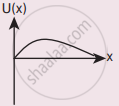
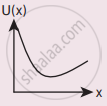
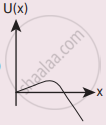
A particle is placed at the origin and a force F = kx is acting on it (where k is a positive constant). If U(0) = 0, the graph of U(x) versus x will be (where U is the potential energy function)
A particle that is constrained to move along the x-axis, is subjected to a force in the same direction which varies with the distance x of the particle from the origin as F(x) = -kx + ax3. Here, k and a are positive constants. For x ≥ 0, the functional form of the potential energy U(x) of the particle is ______
A spring of force constant k is cut into two pieces such that one piece is double the length of the other. Then, the long piece will have a force constant of ______
`2/3`k
`3/2`k
3k
6k
Short Answer Questions
Explain how the definition of work in physics is different from general perception.
Write the various types of potential energy. Explain the formulae.
Write the differences between conservative and Non-conservative forces. Give two examples each.
Explain the characteristics of elastic and inelastic collision.
Define the following:
Coefficient of restitution
Define power.
Define the following:
Law of conservation of energy
Define the following:
loss of kinetic energy in an inelastic collision.
Long Answer Questions
Explain with graphs the difference between work done by a constant force and by a variable force.
State and explain the work-energy principle. Mention any three examples for it.
Arrive at an expression for power and velocity. Give some examples for the same.
Arrive at an expression for elastic collision in one dimension and discuss various cases.
What is inelastic collision? In which way it is different from an elastic collision. Mention a few examples in day-to-day life for inelastic collision.
Numerical Problems
Calculate the work done by a force of 30 N in lifting a load of 2kg to a height of 10 m (g = 10 m s−2)
A ball with a velocity of 5 ms−1 impinges at an angle of 60˚ with the vertical on a smooth horizontal plane. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.5, find the velocity and direction after the impact.
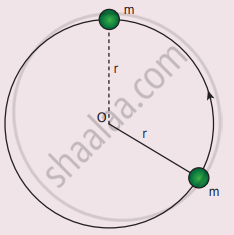
A bob of mass m is attached to one end of the rod of negligible mass and length r, the other end of which is pivoted freely at a fixed center O as shown in the figure. What initial speed must be given to the object to reach the top of the circle? (Hint: Use law of conservation of energy). Is this speed less or greater than the speed obtained in section 4.2.9?
Two different unknown masses A and B collide. A is initially at rest when B has a speed v. After collision B has a speed v/2 and moves at right angles to its original direction of motion. Find the direction in which A moves after the collision.
A bullet of mass 20 g strikes a pendulum of mass 5 kg. The centre of mass of the pendulum rises a vertical distance of 10 cm. If the bullet gets embedded into the pendulum, calculate its initial speed.
Solutions for 4: Work, Energy and Power
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 4 - Work, Energy and Power Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 4 - Work, Energy and Power - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 4 - Work, Energy and Power
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 4 (Work, Energy and Power) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 4 Work, Energy and Power are Introduction to Work, Energy, Power, Collisions.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Work, Energy and Power exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Work, Energy and Power Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Physics - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.