Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
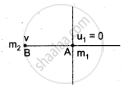
Two different unknown masses A and B collide. A is initially at rest when B has a speed v. After collision B has a speed v/2 and moves at right angles to its original direction of motion. Find the direction in which A moves after the collision.
उत्तर
Given:
`u_2 = v, u_1 = 0`
`v_2 = v/2, theta = ?`
Component along x-axis
`m_1v_1 costheta = m_2v` ..................(1)
Component along y-axis
`m_1v_1 sintheta = m_2(v/2)` ..................(2)
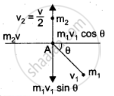
from (1) and (2)
`tan theta = ((v/2))/v = 1/2;`
`theta = tan^-1(1/2) = tan^-1(0.5); theta = 26^circ33^'.`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
In an elastic collision of two bodies, the momentum and energy of each body is conserved.
A molecule in a gas container hits a horizontal wall with speed 200 m s–1 and angle 30° with the normal, and rebounds with the same speed. Is momentum conserved in the collision? Is the collision elastic or inelastic?
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V. If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?

The bob A of a pendulum released from 30° to the vertical hits another bob B of the same mass at rest on a table, as shown in the figure. How high does the bob A rise after the collision? Neglect the size of the bobs and assume the collision to be elastic.

Answer the following question.
Discuss the following as special cases of elastic collisions and obtain their exact or approximate final velocities in terms of their initial velocities.
- Colliding bodies are identical.
- A very heavy object collides on a lighter object, initially at rest.
- A very light object collides on a comparatively much massive object, initially at rest.
During inelastic collision between two bodies, which of the following quantities always remain conserved?
Two blocks M1 and M2 having equal mass are free to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Iniially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2.
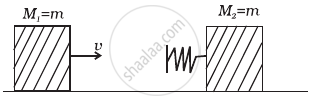
- While spring is fully compressed all the KE of M1 is stored as PE of spring.
- While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum.
- If spring is massless, the final state of the M1 is state of rest.
- If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic.
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, which of the following quantities remain conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact).
- Kinetic energy.
- Total linear momentum?
Give reason for your answer in each case.
An insect moves with a constant velocity v from one corner of a room to other corner which is opposite of the first corner along the largest diagonal of room. If the insect can not fly and dimensions of room is a × a × a, then the minimum time in which the insect can move is `"a"/"v"`. times the square root of a number n, then n is equal to ______.
The dimension of mutual inductance is ______.
