Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
▶ 2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
10: The Nervous System
11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 2 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 2 Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division Review Questions [Pages 19 - 22]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The Chromatin material is formed forms of ______.
DNA only
DNA and Histones
Histones only
Nucleotides
The term “chromosomes” literally means ______.
Inherited bodies
Twisted threads
Coloured bodies
Shining threads
The number of chromosomes in a certain type of cell division is halved. This kind of cell division occurs in ______.
Only testis
Only ovary
Both ovary and testis
All body cells
In which one of the following options the two stages of mitosis have been given in correct sequence?
Prophase, metaphase, telophase, anaphase
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Anaphase, telophase, prophase, metaphase
Telophase, anaphase, prophase, metaphase
In which one of the following options the two stages of mitosis have been given in correct sequence?
Prophase, metaphase, telophase, anaphase
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Anaphase, telophase, prophase, metaphase
Telophase, anaphase, prophase, metaphase
The new cells are to be produced for all except:
Growth
Movement
Repair
Replacement
The chromosomes are duplicated in ______.
M phase
G1 phase
S phase
G2 phase
Triple hydrogen bonds are present between ______.
Adenine and Thymine
Adenine and Cytosine
Adenine and Guanine
Guanine and Cytosine
In the cells of a human male body, the number of autosomes is ______.
23 pairs
22 pairs
1 pair
46 pairs
The basis of genetic variation in the living organisms during mitosis occurs due to ______.
Cell division
Mutation
Crossing over
Karyokinesis
After a mitotic cell division, a human female cell will have ______.
22 + X chromosomes
44 + XY chromosomes
44 + XX chromosomes
22 + XX chromosomes
The correct sequence of phases in interphase is ______.
G1, G2 and S
S, G2 and G1
G1 S and G2
G2, S and G1
The phase of karyokinesis which is almost the reverse of prophase is ______.
Interphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
The lengthwise arrangement of DNA mainly consists of a phosphate group attached with ______.
Hexose sugar
Purines
Pentose sugar
Pyrimidines
The number of histone proteins associated with the DNA in a nucleosome is ______.
6
8
4
1
The pyrimidine bases of DNA are ______.
Adenine and Guanine
Guanine and Cytosine
Adenine and Thymine
Thymine and Cytosine
The female gamete/egg cell of a human cell will have ______.
44 +XX chromosomes
44 + XY chromosomes
22 + X chromosomes
22 + Y chromosomes
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Name the repeating components of each DNA strand lengthwise.
Name the complex consisting of DNA strand and a core of histones.
Name the type of bond which joins the complementary nitrogenous bases.
Name the three components of a nucleotide.
Imagine one cell (A) has undergone one mitotic division and another cell (B) has completed its meiotic division. How many cells would the two produce?
Cell A: ______
Cell B: ______
Match the events given in column A with the phase in mitotic cell division in column B.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ | ||
| 1. | Chromosomes get arranged in a horizontal plane at the equator. |
a. | Anaphase |
| 2. | Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite poles of a spindle |
b. | Prophase |
| 3. | Chromosomes become visible as fine, long threads. |
c. | Telophase |
| 4. | Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually become transformed into a chromatin network. |
d. | Metaphase |
DNA replicates in the ______ of the cell cycle.
Mitosis occurs in our ______ cells.
Meiosis occurs only in __________ cells.
Humans have 46 chromosomes. Their sperms and eggs will have ______ chromosomes each.
During the pairing of chromosomes in meiosis, the ________ chromosomes come to lie side by side.
The two non-sister chromatids of a paired chromosome are attached to each other at ______ during the process of crossing over.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Name these:
Two main constituents of Chromatin
Name these:
Two kinds of Nucleic acids
Name the three components of a nucleotide.
Name these:
Four Nitrogenous bases
Name these:
Two kinds of Nitrogenous bases
Name these:
Two components of Nucleosome
Name the following:
The two kinds of cell division found in living organisms.
Name these:
Four main phases of Karyokinesis
Name these:
Two steps of the process Mitosis
Name these:
Two kinds of haploid cells of human body
Correct the following statement if there is any mistake.
The four nitrogenous bases in the DNA are Guanine, Thiamine, Adrenaline and Cytosine.
Correct the following statement if there is any mistake:
Genes are specific sequences of bases on a chromosome .
Correct the following statement if there is any mistake:
A nucleotide is composed of a sulphate, a sugar (pentose) and a nitrogenous base .
Correct the following statement if there is any mistake:
Nucleosomes are groups of cysteine molecules surrounded by DNA strands.
Correct the following statement if there is any mistake:
If there are 46 chromosomes in a cell, there will be 23 chromatin fibres inside the nucleus during interphase.
DESCRIPTIVE TYPE
Define the following term:
Chromosome
Define the following term:
Gene
Define cell division.
Define the following term:
Chromatid
Define the following term:
Aster
Give a reason for the following:
Gametes must be produced by meiosis for sexual reproduction.
Give reason:
Why is meiosis referred to as 'reductional division'?
Give reason:
The children of the same parents, howsoever similar, are different from each other in certain aspects.
Differentiate between Cytokinesis and Karyokinesis.
Distinguish between the following:
DNA and RNA
Distinguish between the following:
Nucleosome and Nucleotide
Differentiate between Centrosome and centromere.
State the difference between:
Haploid and diploid
Write the full form of the following abbreviation:
DNA
Write the full form of the following abbreviation:
RNA
Given below is a set of four term. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining term:
Adenine
Guanine
Adrenaline
Thymine
Given below is a set of four term. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining term:
Pentose sugar
Histones
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous bases
Given below is a set of four term. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining term:
Metaphase
Anaphase
Interphase
Telophase
Given below is a set of four term. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining term:
G1 phase
M phase
G2 phase
S phase
Given below is a set of four term. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining term:
Chromoplast
Chromosome
Chloroplast
Leucoplast
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
Given below is a schematic diagram of a portion of DNA.
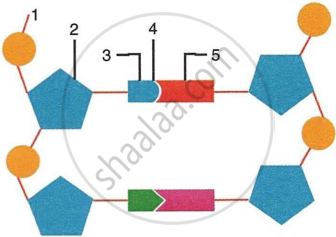
- How many strands are shown in the diagram?
- How many nucleotides have been shown in each strand?
- Name the parts numbered 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively.
- Name the DNA unit constituted by the parts 1, 2, 3 collectively.
The three sketch (A, B and C) are intended to represent the replication of DNA.
What should be their correct sequence, starting with the first and ending with the last? ……

The diagram below represents a stage during cell division. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
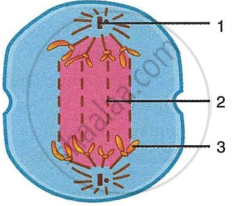
- Name the parts labelled 1, 2, and 3.
- Identify the above stage and give a reason to support your answer.
- Mention where in the body this type of cell division occurs.
- Name the stage prior to this stage and draw a diagram to represent the same.
Draw a labelled diagram to show the metaphase stage of mitosis in an animal cell having ‘6’ chromosomes.
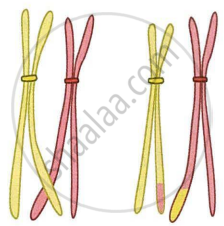
The diagram given below represents a certain phenomenon which occurs during meiosis. Name and explain the phenomenon by using the terms homologous chromosomes, chromatids, crossing over.
Given below is a diagram representing a stage during mitotic cell division in an animal cell Examine it carefully and answer the questions which follow.
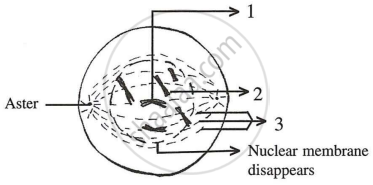
- Identify the stage. Give one reason in support of your answer.
- Name the cell organelle that forms the ‘aster’.
- Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
- Name the stage that follows the one shown above; how is that stage identified?
- Mention two differences between mitosis and meiosis with regards to:
- The number of daughter cells produced.
- The chromosome number in the daughter cells.
Given below are three diagrammatic sketches (A, B and C) of one and the same particular phase during mitotic type of cell division.

- Identify the phase.
- What is the diploid number of chromosomes shown in them?
- Identify whether these are animal cells or plant cells? Give reasons.
- Which of these is/are shown in the correct direction?
- Only A
- Only B
- Only A and C
- All the three
Shown below are four stages (A, B, C, D) (not in sequence) of a certain kind of cell division.

- Is it a plant cell or an animal cell? Give two reasons.
- Is it undergoing mitosis or meiosis?
- What should be the correct sequence of these four stages among themselves?
- Name the stage that should precede the earliest of these stages.
- Draw the stage names above inside the blank space provided.
Solutions for 2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 - Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 2 (Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 2 Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division are Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity, Chromatin, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure, Histone Proteins, Genes and Genetic, Need for New Cells, Cell Cycle - "Divide, Grow and Redivide", Cell Division: an Essential Life Process, Mitosis and Its Phases, Phases of Mitosis: Karyokinesis (Division of Nucleus), Phases of Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm), Meiosis as a Reduction Division, Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis I, Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis II, Significance of Meiosis, Significance of Mitosis, Organisms Show Variety in Cell Number, Shape and Size, Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane), Cell: Structural and Functional Unit of Life, Plant Cell and Animal Cell, Structure of the Cell, Plasma Membrane, Cell Wall - “Supporter and Protector”, Nucleus - “Brain” of the Cell, Cytoplasm - “Area of Movement”, Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), Mitochondria - “Power House of the Cell”, Golgi Apparatus - "The delivery system of the cell", Ribosomes - "The sites of protein synthesis", Lysosome - “Suicidal Bag”, Centrosome and Centrioles, Plastids, Non-living Substances Or Cell Inclusion, Microscopic examination of onion peel, Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity, Chromatin, Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Its Structure, Histone Proteins, Genes and Genetic, Need for New Cells, Cell Cycle - "Divide, Grow and Redivide", Cell Division: an Essential Life Process, Mitosis and Its Phases, Phases of Mitosis: Karyokinesis (Division of Nucleus), Phases of Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Division of Cytoplasm), Meiosis as a Reduction Division, Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis I, Stages of Meiosis: Meiosis II, Significance of Meiosis, Significance of Mitosis.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 2, Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
