Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
10: The Nervous System
▶ 11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 11 - Sense Organ Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 11 - Sense Organ - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Sense Organ
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 11 Sense Organ Progress Check [Pages 149 - 152]
State the functions of the following:
Eyelids
State the functions of the following:
Eyelashes
State the functions of the following:
Tears
State the functions of the following:
Iris
State the functions of the following:
Ciliary muscles
Write in proper sequence the names of all the parts of the human eye through which the light rays coming from an object pass before they form an image on the retina.
Name the following:
Place of best vision in the retina of the eye.
Name the following:
Place of no vision in the retina of the eye.
Name the following:
Kind of retinal cells sensitive to dim light.
Name the following:
The circular opening enclosed by iris.
Name the following:
The fibres which collectively hold the lens in position.
Name the following:
Capacity of the eye to focus at different distances.
The kind of lens required to correct Myopia
Name the following:
The layer of the wall of the eye-ball that corresponds to the black lining of the box of a camera
Give the reason for the following:
Medicines dropped in the eye flow down into the nose.
Give the reason for the following:
A person from bright sunlight outside enters a poorly lit room and feels blinded for a short while.
Categorise the following parts under (i) external, (ii) middle and (iii) internal ear.
Ear drum, hammer, pinna, cochlea, anvil, stirrup, eustachian tube, tympanum, oval window, semi-circular canals.
State the functions of the following:
Semi-circular canals
Give the main function of the following:
Cochlea
State the functions of the following:
Auditory nerve
Human ear is concerned with hearing only.
True
False
Pinna concentrates and directs sound waves towards tympanum.
True
False
Given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the human ear.
- Name the parts numbered 1-6.
- Which parts of the ear shown here are complete.
 |
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 11 Sense Organ Review Questions [Pages 152 - 155]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE (Select the most appropriate option in each case).
The layer in the eye where sensory cells (rods and cones) are located ______.
Conjunctiva
Cornea
Choroid
Retina
The vitamin required for the synthesis of rhodopsin is ______.
Vitamin A
Vitamin B
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
An aperture that controls the passage of light into the eye is ______.
Blind spot
Pupil
Yellow spot
Iris
Tears have an antiseptic property due to the presence of ______.
Lysosome
Aqueous humour
Lysozyme
Vitreous humour
Which of the following is responsible for the adjustment of the size of pupil?
Iris
Sclera
Lens
Choroid
The median canal of cochlea is filled with ______.
Perilymph
Lymph
Endolymph
Tissue fluid
The thin, transparent extension of sclerotic layer found in front of the lens is ______.
Cornea
Cochlea
Conjunctiva
Choroid
The part of the inner ear which is responsible for hearing is ______.
Semicircular canal
Utriculus
Cochlea
Sacculus
The spiral organ possessing sensory cells for hearing is ______.
Ampulla
Semicircular Canal
Vestibule
Organ of Corti
Which of the following structures equalises the air pressure on either side of the tympanum?
Auditory tube
Eustachian tube
Vestibular canal
Tympanic canal
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Name the following:
The photosensitive pigment present in the rods of the retina.
Name the following:
The part which equalises the air pressure in the middle and external ear.
Name the following:
The ear ossicle attached to the tympanum.
Name the following:
The tube which connects the cavity of the middle ear with the throat.
Name the following:
The part of the eye responsible for its shape.
Name the following:
The nerves which transmit impulse from ear to the brain.
Name the following:
The photoreceptors found in the retina of the eye.
Name the following:
The eye defect caused due to shortening of the eye ball from front to back.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Cones : Iodopsim :: Rods : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Eyes: Photoreceptors :: Ears : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Ears: Auditory nerve :: Eyes : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Ear pinna : Auricle :: Inner ear : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Semi-circular canal : Ampulla :: Cochlea : ______.
Match the terms in column I with those in column II and write down the matching pairs.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Conjunctiva | (a) | Viral infection |
| (ii) | Cornea | (b) | Ciliary body |
| (iii) | Choroid | (c) | Spiral-shaped |
| (iv) | Cochlea | (d) | Transparent epithelium |
| (v) | Conjunctivitis | (e) | Suspensory ligament |
| (f) | Contains melanin | ||
| (g) | Transparent but appears black |
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). If false, correct them by changing any one single word in each.
Deafness is caused due to rupturing of the pinna.
True
False
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). If false, correct them by changing any one single word in each.
Semi-circular canals are concerned with static (positional) balance.
True
False
Where is the following located?
Yellow spot
State the Location of:
Lacrimal gland
Mention, where in living organism is the following located and state their main function:
Organ of corti
Where are the following located?
Eustachian canal
Mention the exact location of the following :
Incus
Given below is a set of five parts. Rewrite them in correct sequence.
Cochlea, tympanum, auditory canal, ear ossicles, oval window.
Given below is a set of five parts. Rewrite them in correct sequence.
Conjunctiva, retina, cornea, optic nerve, lens.
Write the main functional activity of the following structure.
Cochlea
Write the main functional activity of the following structure.
Semicircular canal
State the functions of the following:
Iris
Write the main functional activity of the following structure.
Choroid
Write the main functional activity of the following structure.
Ciliary body and suspensory ligament
Complete the following table by filling in the blank spaces.
| Structure | Function | ||
| 1. | ______ | (i) | Transfers impulse from inner ear to brain. |
| 2. | ______ | (ii) | Helps to change the focal length of the eye lens. |
| 3. | ______ | (iii) | Dynamic equilibrium |
Name the following:
Two pigments of the sensory cells.
Name the following:
Two types of adaptations.
Name the following:
Two kinds of accomodations.
Name the following:
Three layers of the eye ball.
Name the eye defects caused due to each of the following:
| Cause | Eye defect | |
| (a) | Lens turns opaque | ______ |
| (b) | Uneven curvature of the cornea | ______ |
| (c) | Deficiency of vitamin A | ______ |
| (d) | Lens loses its flexibility | ______ |
| (e) | Eye ball lengthens from front to back | ______ |
| (f) | Lens becomes too flat | ______ |
DESCRIPTIVE TYPE
Define the following term:
Conjunctiva
Define the following term:
Lysozyme
Define the following term:
Adaptation
Define the term "power of accommodation" of human eye.
Define the following term:
Ear ossicles
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Myopia and Hyperopia (type of lens used for correction).
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Rods and cones (sensitivity).
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Aqueous humour and vitreous humour (location).
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Near and distant accomodation (shape of lens).
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Dark and light adaptation (pigments which will be regenerated).
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Night blindness and colour blindness (sensory cells which cannot function properly).
Give the reason for the following:
Medicines dropped in the eye flow down into the nose.
Give reason:
Three small bones of ear ossicles are advantageous as compared to one single bone for hearing.
Give reason:
Blind spot is considered as 'area of no vision'.
Mention the characteristics of the image that falls on the retina of the eye.
Describe the mechanism of focusing the image of a distant object in your eye when you raise your head after reading a book.
By closing the eyes and gently pressing them by your palms, you may see some specks of brilliant light. How do you get this sensation while there is no light entering your eyes?
Name the three ear ossicles.
How do the three ear ossicles contribute in the mechanism of hearing?
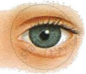
The figures (A) and (B) given below are showing some kind of adjustment. Study the figures and answer the questions that follow.
| A |  |
 |
B |
- Identify the kinds of adjustments done in the figures (A) and (B).
- Distinguish between the adjustments of figures (A) and (B) on the basis of:
- The size of pupil.
- The pigment which gets regenerated.
- Cells of the retina.
With reference to human eye answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the eye associated with the regulation of the size of pupil.
With reference to human eye answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the eye associated with the regulation of the shape of lens.
With reference to human eye answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the eye associated with keeping the lens moist and protecting it from physical shock.
With reference to human eye answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the eye associated with the layer providing nourishment to the eye.
With reference to human ear answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the ear associated with Static balance.
With reference to human ear answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the ear associated with dynamic balance.
With reference to human ear answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the ear associated with hearing.
With reference to human ear answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the ear associated with the amplification of vibrations.
The figure given below refers to the vertical section of the eye of a mammal. Study the figure carefully and answer the following questions.
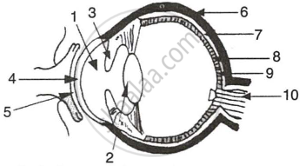 |
- Label the guidelines shown as 1 to 10.
- Write one important role of parts shown as 3 and 7.
- Write one structural difference between the parts shown as 9 and 10.
- Mention one functional difference between the parts shown as 6 and 8.
Given alongside is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
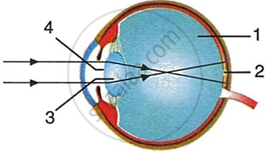 |
- Name the defect shown in the diagram.
- Give two possible reasons for this defect.
- Name the parts labelled 1 to 4.
- Name the type of lens used to correct this eye defect.
- Draw a labelled diagram to show how the above mentioned defect is rectified using the lens named above.
- Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of the membranous labyrinth found in the inner ear.
- Based on the diagram drawn above in (i), give a suitable term for each of the following descriptions:
- The structure responsible for hearing.
- The sensory cells that help in hearing.
- The membrane-covered opening that connects the middle ear to inner ear.
- The nerves that carry impulses from the ear to the brain.
- The tube which equalises the air pressure on either side of the ear drum.
Given below is the diagram of a part of the human ear. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
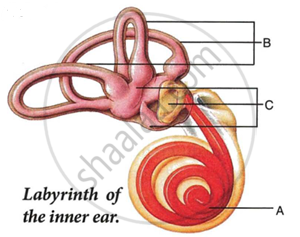 |
- Give the collective biological term for Malleus, locus and Stapes.
- Name the parts labelled A, B and C in the diagram.
- State the functions of the parts labelled 'A' and 'B'.
- Name the audio receptor region present in the part labelled 'A'.
Draw a labelled diagram of the inner ear.
Name the part of the inner ear that is responsible for static balance in human beings.
Have a look at the posture of this girl who is reading a book and answer the questions which follow:
 |
- Name the problem she is facing.
- What are the two conditions shown in sections A and B of the eye as applicable to her.
- What kind of reading glasses does she need?
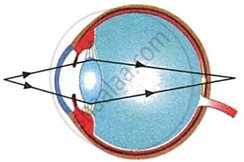 |
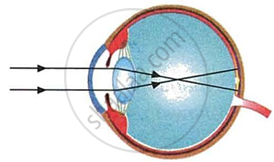 |
| A | B |
The figure given below shows the principal parts of a human ear. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
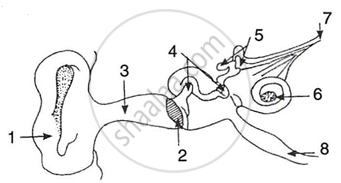 |
- Label the parts 1 to 8.
- State the role of parts 6, 7 and 8.
- Why is it harmful to use a sharp object to remove ear wax? Mention the number and name of the part involved.
Solutions for 11: Sense Organ
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 11 - Sense Organ Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 11 - Sense Organ - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 11 - Sense Organ
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 11 (Sense Organ) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 11 Sense Organ are Sense Organ, The Eyes, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism, Some Common Defects of the Eye, Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision, Functions of the Ear, Human Ear, Sense Organ, The Eyes, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism, Some Common Defects of the Eye, Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision, Functions of the Ear, Human Ear, Major Division of the Nervous System, Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types, Human Nervous System, Nerve Fibres, The Spinal Cord, Reflex and Reflex Action, Transmission of Nerve Impulse, Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres, The Human Brain - Forebrain, Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), Types of Reflexes, Nervous Pathways in Reflexes, Reflex Arc, Complex Reflex Action, Sense Organ, The Eyes, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism, Some Common Defects of the Eye, Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision, Functions of the Ear, Human Ear, Major Division of the Nervous System, Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types, Human Nervous System, Nerve Fibres, The Spinal Cord, Reflex and Reflex Action, Transmission of Nerve Impulse, Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres, The Human Brain - Forebrain, Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), Types of Reflexes, Nervous Pathways in Reflexes, Reflex Arc, Complex Reflex Action, Sense Organ, The Eyes, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism, Some Common Defects of the Eye, Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision, Functions of the Ear, Human Ear.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Sense Organ exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Sense Organ Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
