Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the main functional activity of the following structure.
Choroid
उत्तर
- The choroid layer is richly supplied with blood vessels to nourish the eye.
- It contains a dark black pigment (melanin), which prevents light rays from reflecting and scattering inside the eye.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: ciliary muscles
Answer briefly:
How do you perceive the colour of an object?
Describe the anatomy of the human eye.
What is the least distance of distinct vision for a normal human eye?
A person walking in a dark corridor enters into a brightly lit room:
State the effect on the pupil of the eye.
An object is moved closer to an eye. What changes must take place in the eye in order to keep the image in sharp focus?
Why does the eye-lens not have to do all the work of converging incoming light rays?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Rabbit has eyes which look sideways.
Name two animals having eyes:
one the sides of the head.
The region in the eyes where the rods and cones are located is the
Name the following:
The part of the eye responsible for its shape.
Mention if the following statement is true (T) or false (F) Give reason.
Short-sightedness and hyperopia are one and the same thing
Give scientific reason:
We cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
Define the following:
Power of accommodation
Name the following:
Fluid present in the posterior chamber of the eye.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate Word
The aperture in the eye through which light enters is the:
The following figure show the change in the shape of the lens while seeing distant and nearby objects. Complete the figures by correctly labelling the diagram.
Boojho while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers appear blurred. What could be the reason for it?
Select the option with incorrect identification:
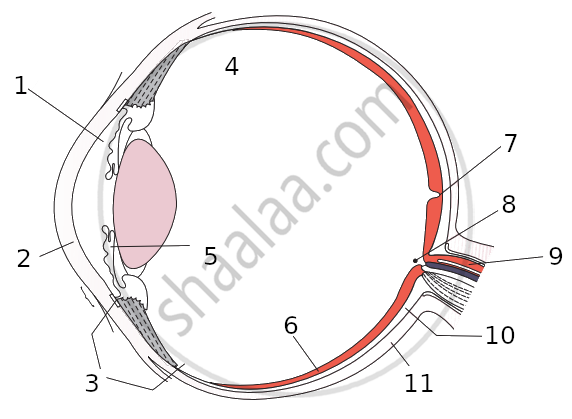
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
