Topics
Mathematics
Knowing Our Numbers
- Introduction to Knowing Our Numbers
- Comparing Numbers
- Compare Numbers in Ascending and Descending Order
- Compare Number by Forming Numbers from a Given Digits
- Compare Numbers by Shifting Digits
- Introducing a 5 Digit Number - 10,000
- Concept of Place Value
- Expansion Form of Numbers
- Introducing the Six Digit Number - 1,00,000
- Introducing seven-digit numbers
- Crores
- Using Commas in Indian and International Number System
- Round off and Estimation of Numbers
- To Estimate Sum Or Difference
- Estimating Products of Numbers
- Simplification of Expression by Using Brackets
- BODMAS - Rules for Simplifying an Expression
Whole Numbers
- Concept for Natural Numbers
- Concept for Whole Numbers
- Successor and Predecessor of Whole Number
- Operation of Whole Numbers on Number Line
- Properties of Whole Numbers
- Closure Property of Whole Number
- Associativity Property of Whole Numbers
- Division by Zero
- Commutativity Property of Whole Number
- Distributivity Property of Whole Numbers
- Identity of Addition and Multiplication of Whole Numbers
- Patterns in Whole Numbers
Playing with Numbers
- Arranging the Objects in Rows and Columns
- Factors and Multiples
- Concept of Perfect Number
- Concept of Prime Numbers
- Concept of Co-Prime Number
- Concept of Twin Prime Numbers
- Concept of Even and Odd Number
- Concept of Composite Number
- Eratosthenes’ method of finding prime numbers
- Tests for Divisibility of Numbers
- Divisibility by 10
- Divisibility by 5
- Divisibility by 2
- Divisibility by 3
- Divisibility by 6
- Divisibility by 4
- Divisibility by 8
- Divisibility by 9
- Divisibility by 11
- Common Factor
- Common Multiples
- Some More Divisibility Rules
- Prime Factorisation
- Highest Common Factor
- Lowest Common Multiple
Basic Geometrical Ideas
- Concept for Basic Geometrical Ideas (2 -d)
- Concept of Points
- Concept of Line
- Concept of Line Segment
- Concept of Ray
- Concept of Intersecting Lines
- Introduction to Parallel Lines
- Concept of Curves
- Different Types of Curves - Closed Curve, Open Curve, Simple Curve.
- Concept of Polygons
- Concept of Angle
- Concept of Triangles
- Concept of Quadrilaterals
- Concept of Circle
Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Introduction to Understanding Elementary Shapes
- Measuring Line Segments
- Right, Straight, and Complete Angle by Direction and Clock
- Concept of Angle
- Measuring Angles
- Perpendicular Line and Perpendicular Bisector
- Classification of Triangles (On the Basis of Sides, and of Angles)
- Classification of Triangles based on Sides- Equilateral, Isosceles, Scalene
- Classification of Triangles based on Angles: Acute-Angled, Right-Angled, Obtuse-Angled
- Types of Quadrilaterals
- Properties of a Square
- Properties of Rectangle
- Properties of a Parallelogram
- Properties of Rhombus
- Properties of Trapezium
- Three Dimensional Shapes
- Prism
- Concept of Pyramid
- Concept of Polygons
Integers
Fractions
Decimals
- The Decimal Number System
- Concept of Place Value
- Concept of Tenths, Hundredths and Thousandths in Decimal
- Representing Decimals on the Number Line
- Conversion between Decimal Fraction and Common Fraction
- Comparing Decimal Numbers
- Using Decimal Number as Units
- Addition of Decimal Fraction
- Subtraction of Decimal Fraction
Data Handling
Mensuration
Algebra
Ratio and Proportion
Symmetry
Practical Geometry
- Introduction to Geometric Tool
- Construction of a Circle When Its Radius is Known
- Construction of a Line Segment of a Given Length
- Constructing a Copy of a Given Line Segment
- Drawing a Perpendicular to a Line at a Point on the Line
- Drawing a perpendicular to a line from a point outside the line
- The Perpendicular Bisector
- Constructing an Angle of a Given Measure
- Construction of an angle bisector using a compass
- Concept of Angle Bisector
- Angles of Special Measures - 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, and 120°
Notes
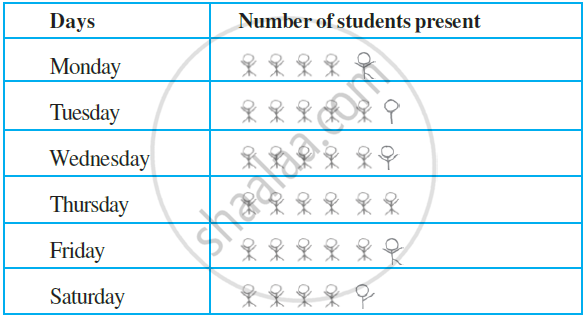
Drawing a Pictograph:
The following are the details of the number of students present in a class of 30 during a week. Represent it by a pictograph.
| Days | Number of students present |
| Monday | 24 |
| Tuesday | 26 |
| Wednesday | 28 |
| Thursday | 30 |
| Friday | 29 |
| Saturday | 22 |
With the assumptions, we have made earlier,
24 may be represented by 
26 may be represented by  and so on.
and so on.
Thus, the pictograph would be
Example
Total number of animals in five villages are as follows:
Village A: 80
Villages B: 120
Village C: 90
Village D: 40
Village E: 60
Prepare a pictograph of these animals using one symbol ⊗ to represent 10 animals and answer the following questions:
(a) How many symbols represent animals of village E?
(b) Which village has the maximum number of animals?
(c) Which village has more animals: village A or village C?
The pictograph for the given data can be drawn as follows.
|
Village |
Number of animals ⊗ − 10 animals |
|
Village A |
⊗⊗⊗⊗⊗⊗⊗⊗ |
|
Village B |
⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ |
|
Village C |
⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ |
|
Village D |
⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ |
|
Village E |
⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ ⊗ |
(a) 6 symbols will represent animals of village E as there were 60 animals in this village.
(b) Village B has the maximum number of animals i.e., 120.
(c) Village A and C have 80 and 90 animals in it. Clearly, Village C has more animals.
Shaalaa.com | Drawing a Pictography
Related QuestionsVIEW ALL [14]
Draw a pictograph for the given data.
| Month | June | July | August | September |
| Number of Computers sold | 300 | 450 | 600 | 550 |
(Choose your own suitable scale)
The following table shows the number of tourists who visited the places in the month of May. Draw a pictograph
| Place | Mahabalipuram | Vedanthangal | Hogenakkal | Ooty |
| Number of Tourists | 20,000 | 15,000 | 40,000 | 35,000 |
(Choose your own suitable scale)
The total number of students of a school in different years is shown in the following table
| Years | Number of students |
| 1996 | 400 |
| 1998 | 535 |
| 2000 | 472 |
| 2002 | 600 |
| 2004 | 623 |
Prepare a pictograph of students using one symbol 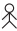 to represent 100 students and answer the following questions:
to represent 100 students and answer the following questions:
How many symbols represent the total number of students in the year 2002?
Neela, Mala, Kala and Bala were neighbours. The following data shows the number of fish in each of their fish tank. Draw pictograph to represent the data and Answer the questions.
| Neela | Mala | Kala | Bala |
| 16 | 20 | 12 | 24 |
a. How many fishes did bala have? ___________
b. Who has 16 fishes? ___________
c. How many fewer fish did Kala have than Mala? _____________
d. How many fish did Neela and Bala have altogether? ______________
The following Pictograph shows the number of students playing different games in a school.
| Game | Number of Students |
| Kho-Kho |  |
| Kabaddi |  |
| Basketball |  |
| Volleyball |  |
| Hockey |  |
 Represents 10 students
Represents 10 students
Answer the following questions.
(i) Which is the most popular game among the students?
(ii) Find the number of students playing Kabaddi.
(iii) Which two games are played by equal number of students?
(iv) What is the difference between the number of students playing Kho-Kho and Hockey?
(v) Which is the least popular game among the students?
There are 1000 students in a school. Data regarding the mode of transport of the students is given below. Draw a pictograph to represent the data.
| Mode of Travel | On Foot | Bicycle | Scooter | Bus | Car |
| Number of Students | 350 | 300 | 150 | 100 | 100 |
Yasmin of class VI was given a task to count the number of books which are biographies, in her school library. The information collected by her is represented as follows.
| Biographies | Number of books |
| Mathematicians |  |
| Scientists |  |
| Novelists |  |
| Sportspersons |  |
| Politicians |  |
Keys: 
Observe the pictograph and answer the following questions.
(i) Which title has the maximum number of biographies?
(ii) Which title has the minimum number of biographies?
(iii) Which title has exactly half the number of biographies as Novelists?
(iv) How many biographies are there on the title of Sportspersons?
(v) What is the total number of biographies in the library?
