Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v0, collides inelastically (e > 0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that for a general collision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less than 90°.
उत्तर
Consider the diagram below for a general collision.

By the principle of conservation of linear momentum,
P = P1 + P2
For inelastic collision, some KE is lost, hence `p^2/(2m) > p_1^2/(2m) + p_2^2/(2m)`
∴ `p^2 > p_1^2 + p_2^2`
Thus, p, p1 and p2 are related as shown in the figure.
θ is acute (less than 90) `(p^2 = p_1^2 + p_2^2 "would given" θ = 90^circ)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the quantities which do not change after the collision are the ______ of the system of two bodies.
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V. If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?

Answer the following question.
Discuss the following as special cases of elastic collisions and obtain their exact or approximate final velocities in terms of their initial velocities.
- Colliding bodies are identical.
- A very heavy object collides on a lighter object, initially at rest.
- A very light object collides on a comparatively much massive object, initially at rest.
Solve the following problem.
A spring ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from some height. On falling freely for 10 s, it explodes into two fragments of mass ratio 1:2. The lighter fragment continues to travel downwards with a speed of 60 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy supplied during the explosion.
What is inelastic collision? In which way it is different from an elastic collision. Mention a few examples in day-to-day life for inelastic collision.
In inelastic collision, ____________.
A smooth sphere of mass 'M' moving with velocity 'u' directly collides elastically with another sphere of mass 'm' at rest. After collision, their final velocities are V' and V respectively. The value of V is given by ______.
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in figure.
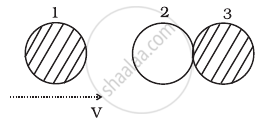
If the collision is elastic, which of the following (Figure) is a possible result after collision?
A ball falls from a height of 1 m on a ground and it loses half its kinetic energy when it hits the ground. What would be the total distance covered by the ball after sufficiently long time?
Three identical blocks A, B and C are placed on horizontal frictionless surface. The blocks A and C are at rest. But A is approaching towards B with a speed 10 m/s. The coefficient of restitution for all collision is 0.5. The speed of the block C just after the collision is ______.

