Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v0, collides inelastically (e > 0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that for a general collision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less than 90°.
Solution
Consider the diagram below for a general collision.

By the principle of conservation of linear momentum,
P = P1 + P2
For inelastic collision, some KE is lost, hence `p^2/(2m) > p_1^2/(2m) + p_2^2/(2m)`
∴ `p^2 > p_1^2 + p_2^2`
Thus, p, p1 and p2 are related as shown in the figure.
θ is acute (less than 90) `(p^2 = p_1^2 + p_2^2 "would given" θ = 90^circ)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
A bullet of mass m1 travelling with a velocity u strikes a stationary wooden block of mass m2 and gets embedded into it. Determine the expression for loss in the kinetic energy of the system. Is this violating the principle of conservation of energy? If not, how can you account for this loss?
What is inelastic collision? In which way it is different from an elastic collision. Mention a few examples in day-to-day life for inelastic collision.
A body of mas 'm' moving with speed 3 m/s collides with a body of mass '2m' at rest. The coalesced mass will start to move with a speed of ______.
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in figure.
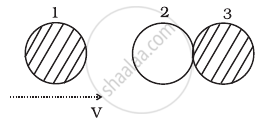
If the collision is elastic, which of the following (Figure) is a possible result after collision?
The bob A of a pendulum released from horizontal to the vertical hits another bob B of the same mass at rest on a table as shown in figure.
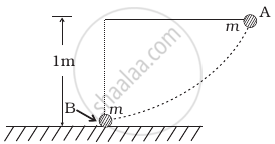
If the length of the pendulum is 1 m, calculate
- the height to which bob A will rise after collision.
- the speed with which bob B starts moving. Neglect the size of the bobs and assume the collision to be elastic.
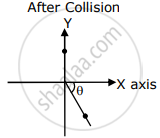
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity of 10`sqrt3` ms–1 along the X-axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y-axis at a speed of 10 m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle θ (degree) with respect to the X-axis.
The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure.
The value of θ to the nearest integer is ______.
A ball is thrown upwards from the foot of a tower. The ball crosses the top of tower twice after an interval of 4 seconds and the ball reaches ground after 8 seconds, then the height of tower is ______ m. (g = 10 m/s2)
An insect moves with a constant velocity v from one corner of a room to other corner which is opposite of the first corner along the largest diagonal of room. If the insect can not fly and dimensions of room is a × a × a, then the minimum time in which the insect can move is `"a"/"v"`. times the square root of a number n, then n is equal to ______.
The dimension of mutual inductance is ______.
Answer carefully, with reason:
Is the total linear momentum conserved during the short time of an inelastic collision of two balls ?
