Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Consider a one-dimensional motion of a particle with total energy E. There are four regions A, B, C and D in which the relation between potential energy V, kinetic energy (K) and total energy E is as given below:
Region A : V > E
Region B : V < E
Region C : K > E
Region D : V > K
State with reason in each case whether a particle can be found in the given region or not.
Solution
We know that
Total energy E = PE + KE
⇒ E = V + K ......(i)
For region A Given, V > E, From equation (i)
K = E – V
As V > E ⇒ E – V < 0
Hence, K < 0, this is not possible.
For region B Given, V < E ⇒ E – V > 0
This is possible because total energy can be greater than PE(V)
For region C Given, K > E ⇒ K – E > 0
From equation (i) PE = V = E – K < 0
This is possible because PE can be negative.
For region D Given, V > K
This is possible because for a system PE (V) may be greater than KE (K).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V. If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?

Solve the following problem.
A ball of mass 100 g dropped on the ground from 5 m bounces repeatedly. During every bounce, 64% of the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. Calculate the following:
- Coefficient of restitution.
- The speed with which the ball comes up from the ground after the third bounce.
- The impulse was given by the ball to the ground during this bounce.
- Average force exerted by the ground if this impact lasts for 250 ms.
- The average pressure exerted by the ball on the ground during this impact if the contact area of the ball is 0.5 cm2.
Explain the characteristics of elastic and inelastic collision.
A ball is thrown vertically down from height of 80 m from the ground with an initial velocity 'v'. The ball hits the ground, loses `1/6`th of its total mechanical energy, and rebounds back to the same height. If the acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2, the value of 'v' is
A wooden block of mass 'M' moves with velocity 'v ' and collides with another block of mass '4M' which is at rest. After collision, the block of mass 'M' comes to rest. The coefficient of restitution will be ______.
A bullet fired from gun with a velocity 30 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal direction. At the highest point of its path, the bullet explodes into two parts with masses in the ratio 1:3. The lighter mass comes to rest immediately. Then the speed of the heavier mass is
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in figure.
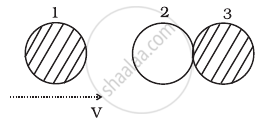
If the collision is elastic, which of the following (Figure) is a possible result after collision?
The bob A of a pendulum released from horizontal to the vertical hits another bob B of the same mass at rest on a table as shown in figure.
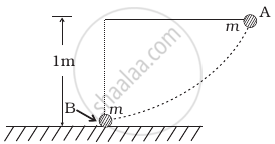
If the length of the pendulum is 1 m, calculate
- the height to which bob A will rise after collision.
- the speed with which bob B starts moving. Neglect the size of the bobs and assume the collision to be elastic.
A drunkard walking in a narrow lane takes 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, followed again by 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, and so on. Each step is 1 m long and required 1 s to cover. How long the drunkard takes to fall in a pit 13 m away from the start?
Three identical blocks A, B and C are placed on horizontal frictionless surface. The blocks A and C are at rest. But A is approaching towards B with a speed 10 m/s. The coefficient of restitution for all collision is 0.5. The speed of the block C just after the collision is ______.

