Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
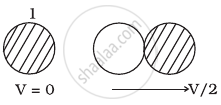
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in figure.
If the collision is elastic, which of the following (Figure) is a possible result after collision?
Options
Solution
Explanation:
In a collision, if the motion of colliding particles before and after the collision is along the same line, the collision is said to be head-on or one-dimensional.
When two bodies of equal masses collide elastically, their velocities are interchanged.
Kinetic energy and linear momentum remain conserved Total kinetic energy of the system before the collision
= `1/2 mv^2 + 0 = 1/2 mv^2`
In (a), kinetic energy of the system after the collision.
`k_1 = 1/2 (2m) (v/2)^2 = 1/4 mv^2`
Hence this option is incorrect.
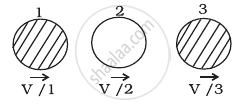
In (b), kinetic energy of the system after the collision.
`k_2 = 1/2 (m) (v)^2 = 1/2 mv^2`
Hence this option will be correct.
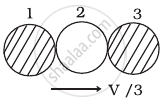
In (c), kinetic energy of the system after the collision.
`k_3 = 1/2 (3m) (v/3)^2 = 1/6 mv^2`
Hence this option is incorrect.
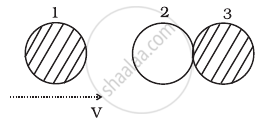
In (d), kinetic energy of the system after the collision.
`k_4 = 1/2 mv^2 + 1/2 m (v/2)^2 + 1/2 m(v/3)^2 = 49/72 mv^2`
We see that kinetic energy is conserved only in (b).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the quantities which do not change after the collision are the ______ of the system of two bodies.
Answer the following question.
A bullet of mass m1 travelling with a velocity u strikes a stationary wooden block of mass m2 and gets embedded into it. Determine the expression for loss in the kinetic energy of the system. Is this violating the principle of conservation of energy? If not, how can you account for this loss?
Solve the following problem.
A ball of mass 100 g dropped on the ground from 5 m bounces repeatedly. During every bounce, 64% of the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. Calculate the following:
- Coefficient of restitution.
- The speed with which the ball comes up from the ground after the third bounce.
- The impulse was given by the ball to the ground during this bounce.
- Average force exerted by the ground if this impact lasts for 250 ms.
- The average pressure exerted by the ball on the ground during this impact if the contact area of the ball is 0.5 cm2.
A ball is thrown vertically down from height of 80 m from the ground with an initial velocity 'v'. The ball hits the ground, loses `1/6`th of its total mechanical energy, and rebounds back to the same height. If the acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2, the value of 'v' is
A ball moving with velocity 5 m/s collides head on with another stationary ball of double mass. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.8, then their velocities (in m/s) after collision will be ____________.
A cricket ball of mass 150 g moving with a speed of 126 km/h hits at the middle of the bat, held firmly at its position by the batsman. The ball moves straight back to the bowler after hitting the bat. Assuming that collision between ball and bat is completely elastic and the two remain in contact for 0.001s, the force that the batsman had to apply to hold the bat firmly at its place would be ______.
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, which of the following quantities remain conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact).
- Kinetic energy.
- Total linear momentum?
Give reason for your answer in each case.
Two pendulums with identical bobs and lengths are suspended from a common support such that in rest position the two bobs are in contact (Figure). One of the bobs is released after being displaced by 10° so that it collides elastically head-on with the other bob.

- Describe the motion of two bobs.
- Draw a graph showing variation in energy of either pendulum with time, for 0 ≤ t ≤ 2T, where T is the period of each pendulum.
A ball is thrown upwards from the foot of a tower. The ball crosses the top of tower twice after an interval of 4 seconds and the ball reaches ground after 8 seconds, then the height of tower is ______ m. (g = 10 m/s2)
A sphere of mass 'm' moving with velocity 'v' collides head-on another sphere of same mass which is at rest. The ratio of final velocity of second sphere to the initial velocity of the first sphere is ______. ( e is coefficient of restitution and collision is inelastic)