Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A faulty balance of equal arms but pans of unequal weight is used to find the weight of a body. By the method of double weighing the weights are found as 8 kg and 8.2 kg. Find the actual weight of the body.
उत्तर

m0= actual weight
mL = weight of leftpan
mR = weight of right pan
mL + 8 = m0 + mR
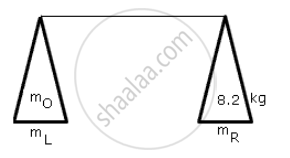
mR + 8.2 kg = m0 + m2
adding the two equations
mL + mR + 16.2kg = 2m0 + m2 +mR
⇒ 16.2 = 2m0
m0 = 8.1 kg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What do you mean by an equilibrium of a body?
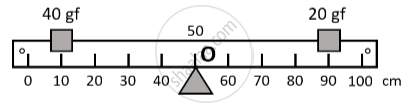
The figure shows a uniform metre rule placed on a fulcrum at its mid-point O and having a weight 40 gf at the 10 cm mark and a weight of 20 gf at the 90 cm mark.
- Is the metre rule in equilibrium? If not how will the rule turn?
- How can the rule be brought in equilibrium by using an additional weight of 40 gf?
State the principle of moments. A meter scale is pivoted at 30 cm mark and it is in equilibrium when a mass of 40 g is suspended from 10 cm mark. Calculate the mass of the ruler.
A faulty balance of unequal arms and pans of unequal weights is used to find the true weight of a metal. By double weighing the weights are found to be 1210 g and 1000 g. Calculate the true weight of the metal.
Define the term momentum.
What is the weight of a body placed at the centre of the earth?
What is meant by equilibrium and state the conditions of equilibrium of a body?
What do you mean by dynamic and static equilibrium? Give one example of each.
One end of a spring is kept fixed while the other end is stretched by a force as shown in the diagram.
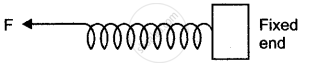
(i) Copy the diagram and mark on it the direction of the restoring force.
(ii) Name one instrument which works on the above principle.
