Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A heater coil is to be constructed with a nichrome wire (ρ = 1.0 × 10−6 Ωm) that can operate at 500 W when connected to a 250 V supply. (a) What would be the resistance of the coil? (b) If the cross-sectional area of the wire is 0.5 mm2, what length of the wire will be needed? (c) If the radius of each turn is 4.0 mm, how many turns will be there in the coil?
उत्तर
(a) Let R be the resistance of the coil.
The power P consumed by a coil of resistance R when connected across a supply V is given by
\[P = \frac{V^2}{R}\]
\[ \Rightarrow R = \frac{V^2}{P}\]
\[ \Rightarrow R = \frac{\left( 250 \right)^2}{500} = 125 \Omega\]
(b) We know:-
\[R = \rho\frac{l}{A}\]
\[ \Rightarrow l = \frac{RA}{\rho}\]
\[ \Rightarrow l = \frac{125 \times 0 . 5 \times {10}^{- 6}}{{10}^{- 6}} = 62 . 5 m\]
(c) Let n be the number of turns in the coil. Then,
\[l = 2\pi rn\]
\[ \Rightarrow n = \frac{l}{2\pi r}\]
\[ \Rightarrow n = \frac{62 . 5}{2 \times 3 . 14 \times 4 \times {10}^{- 3}} \approx 2500\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term 'conductivity' of a metallic wire. Write its SI unit.
Define the term 'electrical conductivity' of a metallic wire. Write its S.I. unit.
The following figure shows a conductor of length l with a circular cross-section. The radius of the cross-section varies linearly from a to b. The resistivity of the material is ρ. Assuming that b – a << l, find the resistance of the conductor.

The heat developed in a system is proportional to the current through it.
An electrolysis experiment is stopped and the battery terminals are reversed.
For a metallic conductor, what is the relation between current density (J), conductivity (σ) and electric field intensity (E)?
In Figure 3 given below, find the value of resistance x for which points A and B are at the same potential:
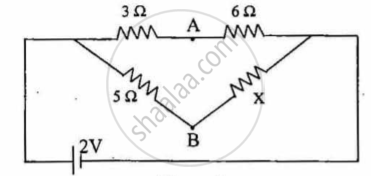
figure 3
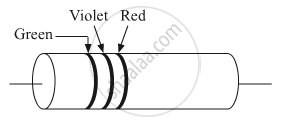
A carbon resistor is shown in the figure. Using color code, write the value of the resistance.
Fill in the blank.
The ___________, a property of materials C, Si, and Ge depends upon the energy gap between their conduction and valence bands.
Consider a current carrying wire (current I) in the shape of a circle.
The electric resistance of a certain wire of iron is R. If its length and radius are both doubled, then ______.
A constant voltage is applied between the two ends of a uniform metallic wire, heat ‘H’ is developed in it. If another wire of the same material, double the radius and twice the length as compared to the original wire is used then the heat developed in it will be -
As the temperature of conductor increase, it's resistivity and conductivity change. The ratio of resistivity to conductivity.
The resistivity of a wire ______
Consider four conducting materials copper, tungsten, mercury and aluminium with resistivity ρC, ρT, ρM and ρA respectively. Then:
