Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A man wearing glasses of focal length +1 m cannot clearly see beyond 1 m
पर्याय
if he is farsighted
if he is nearsighted
if his vision is normal
in each of these cases
उत्तर
in each of these cases
The man is wearing glasses of positive power (converging lens). Hence, he cannot see nearby objects clearly. In other words, he is farsighted. Since he cannot see beyond 1 m, he is nearsighted. If a person with normal vision wears glasses of focal length +1 m, then the person will not be able to see beyond 1 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A virtual image, we always say, cannot be caught on a screen. Yet when we ‘see’ a virtual image, we are obviously bringing it on to the ‘screen’ (i.e., the retina) of our eye. Is there a contradiction?
Does short-sightedness (myopia) or long-sightedness (hypermetropia) imply necessarily that the eye has partially lost its ability of accommodation? If not, what might cause these defects of vision?
What should be the distance between the object and the magnifying glass if the virtual image of each square in the figure is to have an area of 6.25 mm2. Would you be able to see the squares distinctly with your eyes very close to the magnifier?
The angle subtended at the eye by an object is equal to the angle subtended at the eye by the virtual image produced by a magnifying glass. In what sense then does a magnifying glass provide angular magnification?
In viewing through a magnifying glass, one usually positions one’s eyes very close to the lens. Does angular magnification change if the eye is moved back?
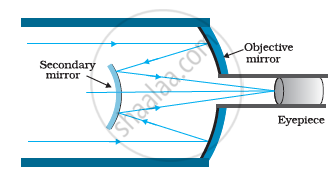
A Cassegrain telescope uses two mirrors as shown in the figure. Such a telescope is built with the mirrors 20 mm apart. If the radius of curvature of the large mirror is 220 mm and the small mirror is 140 mm, where will the final image of an object at infinity be?
The muscles of a normal eye are least strained when the eye is focussed on an object
A person A can clearly see objects between 25 cm and 200 cm. Which of the following may represent the range of clear vision for a person B having muscles stronger than A, but all other parameters of eye identical to that of A?
The focal length of a normal eye-lens is about
The distance of the eye-lens from the retina is x. For a normal eye, the maximum focal length of the eye-lens
When we see an object, the image formed on the retina is
(a) real
(b) virtual
(c) erect
(d) inverted
Mark the correct options.
(a) If the far point goes ahead, the power of the divergent lens should be reduced.
(b) If the near point goes ahead, the power of the convergent lens should be reduced.
(c) If the far point is 1 m away from the eye, divergent lens should be used.
(d) If the near point is 1 m away from the eye, divergent lens should be used.
A person looks at different trees in an open space with the following details. Arrange the trees in decreasing order of their apparent sizes.
| Tree | Height(m) | Distance from the eye(m) |
| A | 2.0 | 50 |
| B | 2.5 | 80 |
| C | 1.8 | 70 |
| D | 2.8 | 100 |
Can virtual image be formed on the retina in a seeing process?
A nearsighted person cannot see beyond 25 cm. Assuming that the separation of the glass from the eye is 1 cm, find the power of lens needed to see distant objects.
