Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न

A metal rod AB of length 80 cm is balanced at 45 cm from the end A with 100 gf weights suspended from the two ends.
- If this rod is cut at the centre C, then compare the weight of AC to the weight of BC.
- Give a reason for your answer in (a).
उत्तर
- Weight of AC < weight of BC.
-
Even though the weights present are the same at both ends, the torque arm of B is less than the torque arm of A. This means the moment of the weight of the rod acts from side B and the C.G. lies beyond 45. Thus, more weight is concentrated between C to B.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are non-contact forces? Give two example
Write an expression for the change in momentum of a body of mass m moving with velocity v if v << c.
A uniform metre rule of weight 10gf is pivoted at its 0 mark.
What moment of force depresses the rule?
What is the work done when no net force is applied on the body?
Calculate the resultant moment of forces about O and state its direction in fig.
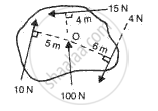
Fig. shows a uniform meter scale weighing 100 N pivoted at its centre. Two weights of 500 N and 300 N are hung from the ruler as shown in fig.
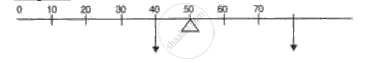
(i) Calculate total clockwise and anticlockwise moments.
(ii) Calculate difference in clockwise moment and anticlockwise moment.
(iii) Calculate the distance from O where a 100 N weight should be suspended to balance the meter scale.
A jack screw is provided with a long arm. Explain why?
A uniform metre scale is balanced at a 40 cm mark when weights of 20 gf and 5 gf are suspended at 5 cm mark and 75 cm mark respectively. Calculate the weight of metre scale.
A couple of 15 N force acts on a rigid body, such that arm of couple is 85 cm. Calculate moment of couple in the SI system.
On a see-saw, two children of masses 30 kg and 50 kg are sitting on one side of it at distance 2 m and 2.5 m respectively, from its middle, where should a man of mass 74 kg sit to balance it?
