Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle of mass 100 g is kept on the surface of a uniform sphere of mass 10 kg and radius 10 cm. Find the work to be done against the gravitational force between them to take the particle away from the sphere.
उत्तर
The work done against the gravitational force to take the particle away from the sphere to infinity is equal to the difference between the potential energy of the particle at infinity and potential energy of the particle at the surface of the sphere.
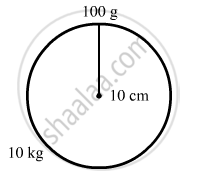
\[\therefore W = 0 - \left( - \frac{G \times 10 \times 0 . 1}{1 \times 0 . 1} \right)\]
\[ = \frac{6 . 67 \times {10}^{- 11} \times 1}{1 \times 0 . 1}\]
\[ = 6 . 67 \times {10}^{- 10} J\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the masses of both objects are doubled?
Which of the Kepler’s laws of planetary motion led Newton to establish the inverse-square rule for gravitational force between two bodies ?
A person sitting in a chair in a satellite feels weightless because
Three equal masses m are placed at the three corners of an equilateral triangle of side a. Find the force exerted by this system on another particle of mass m placed at (a) the mid-point of a side, (b) at the centre of the triangle.
Two small bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg are kept a distance 1.0 m apart and released. Assuming that only mutual gravitational forces are acting, find the speeds of the particles when the separation decreases to 0.5 m.
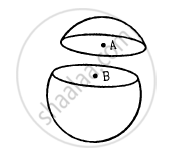
A thin spherical shell having uniform density is cut in two parts by a plane and kept separated as shown in the following figure. The point A is the centre of the plane section of the first part and B is the centre of the plane section of the second part. Show that the gravitational field at A due to the first part is equal in magnitude to the gravitational field at B due to the second part.
Distinguish between gravity and gravitation
Why don't you feel the force of attraction between your friend sitting close to you and yourself?
Where will you weigh more: at the moon's surface or at the earth's surface?
What does a force do in the following case?
You twist a piece of rubber.
The _______ force is much weaker than other forces in nature.
Mahendra and Virat are sitting at a distance of 1 m from each other.Their masses are 75 kg and 80 kg respectively. What is the gravitational force between them? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2)
The force of gravitation between two bodies of mass 1 kg each separated by a distance of 1 m in vacuum is ____________.
Law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between
Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = ½ (BC). m is much-much smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Figure). At subsequent times before any collision takes place ______.

Complete the chart below.
| F(N) | M1(kg) | M2(kg) | D(m) |
| (a) | 50 | 84 | 02 |
| 16 × 109 | 1.63 × 1022 | (b) | 34 |
Observe the figure and answer the questions:
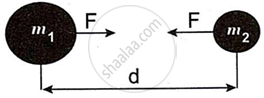
- State Newton's universal law of gravitation.
- If the distance between the two bodies is tripled, how will the gravitational force between them change?
- What will happen to gravitational force, if mass of one of the object is doubled?
