Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A p.d. of 4 V is applied to two resistors of 6 Ω and 2 Ω connected in series. Calculate:
(a) the combined resistance
(b) the current flowing
(c) the p.d. across the 6 Ω resistor
उत्तर
(a) When two resistors are connected in series, their resultant resistance is given by
R = R1+ R2
Here, R1=6Ω ,
R2=2 Ω
Therefore
The resulatant resistance, R = 6 + 2 = 8 Ω
(b) The current flowing through circuit is:
V = IR
I = V/R = 4/8
I = 0.5 A
(c) The p.d. across the 6 Ω resistor is:
V = 0.5 A x 6 Ω = 3 V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the equivalent resistance between points A and B.
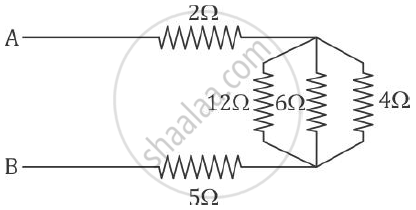
Find the equivalent resistance between A and B

How does the resistance of a wire change when:
its diameter is tripled?
If two resistors of 25 Ω and 15 Ω are joined together in series and then placed in parallel with a 40 Ω resistor, the effective resistance of the combination is :
(a) 0.1 Ω
(b) 10 Ω
(c) 20 Ω
(d)40 Ω
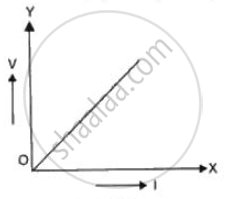
A graph is plotted taking p.d. along y-axis and electric current along x-axis. Name the physical quantity that represents the slope of this graph (Fig.).
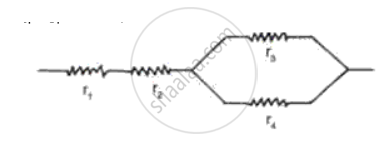
Calculate the equivalent resistance of the following combination of resistor r1, r2, r3, and r4
Define the term resistivity and state its S.I. unit. Which will have higher resistivity a conductor or an insulator.
The resistance of two resistors joined in series is 8Ω and in parallel is 1.5Ω. Find the value of the two resistances.
What is the maximum resistance which can be made using five resistors each of `1/5` W?
