Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A point charge +Q is placed at point O, as shown in the figure. Is the potential difference VA – VB positive, negative or zero?

उत्तर
Electric potential at a distance r from the point charge +Q is given by
`V(r) = 1/(4πε_0) Q/R`
Potential at point A will be
`V(r_A) = 1/(4πε_0) Q/r_A`
Similarly, potential at point B will be
`V(r_B) = 1/(4πε_0) Q/r_A`
`because r_A < r_B`
`therefore V_A > V_B`
`therefore V_A - V_B > 0`
संबंधित प्रश्न
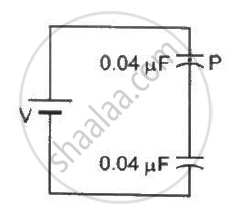
The particle P shown in figure has a mass of 10 mg and a charge of −0⋅01 µC. Each plate has a surface area 100 cm2 on one side. What potential difference V should be applied to the combination to hold the particle P in equilibrium?
Show that electric potential at a point P, at a distance 'r' from a fixed point charge Q, is given by:
`v=(1/(4pi∈_0))Q/r`.
Answer the following question.
The magnitude of the electric field (in NC – 1) in a region varies with the distance r(in m) as
E = 10r + 5
By how much does the electric potential increase in moving from point at r = 11 m to a point at r = 10 m.
Electric potential energy of two point charges q and q0 is ________.
It becomes possible to define potential at a point in an electric field because electric field ______.
A cube of metal is given a positive charge Q. For this system, which of the following statements is true?
From a point charge, there is a fixed point A. At A, there is an electric field of 500 V/m and potential difference of 3000 V. Distance between point charge and A will be ______.
-
The metal plate divides the capacitor into two capacitors connected in parallel to each other.
-
The metal plate divides the capacitors into two capacitors connected in series with each other.
-
The metal plate is equivalent to a dielectric of zero dielectric constant.
A test charge is moved from lower potential point to a higher potential point. The potential energy of test charge will ______.
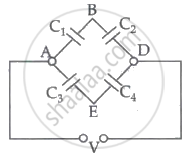
The potential difference between points B and E of the circuits is ______.