Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
(i) A ray of light incident on face AB of an equilateral glass prism, shows minimum deviation of 30°. Calculate the speed of light through the prism.
(ii) Find the angle of incidence at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC.
उत्तर
(i) μ = `sin((A + δ_m)/2)/(sin(A/2))`
= `(sin((60 + 30)/2))/(sin(60^circ/2))`
= `sqrt(2)`
Also μ = `c/v`
⇒ v = `(3 xx 10^8)/sqrt(2)` m/s
(ii)
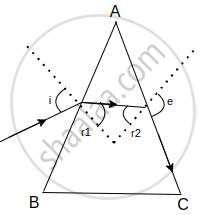
At face AC, let the angle of incidence be r2. For grazing ray, e = 90°
⇒ μ = `1/sinr_2`
⇒ r2 = `sin^-1(1/sqrt(2))` = 45°
Let the angle of refraction at face AB be r1.
Now r1 + r2 = A
∴ r1 = A – r2 = 60º – 45º = 15º
Let the angle of incidence at this face be i
μ = `sini/sin r_1`
⇒ `sqrt(2) = sini/sin15^circ`
∴ i = `sin^-1 (sqrt(2).sin15^circ)` = 21.5º
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two important properties of photon which are used to write Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
Radiation of frequency 1015 Hz is incident on two photosensitive surface P and Q. There is no photoemission from surface P. Photoemission occurs from surface Q but photoelectrons have zero kinetic energy. Explain these observations and find the value of work function for surface Q.
Write the basic features of photon picture of electromagnetic radiation on which Einstein’s photoelectric equation is based.
Plot a labelled graph of |Vs| where Vs is stopping potential versus frequency f of the incident radiation. State how will you use this graph to determine the value of Planck's constant?
Radiations of two photon's energy, twice and ten times the work function of metal are incident on the metal surface successively. The ratio of maximum velocities of photoelectrons emitted in two cases is:
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons from a metal Vs the frequency of the incident radiation gives as straight the whose slope:
What will be wavelength of a photon of momentum 6.6 × 10–24 kgms–1?
What is the momentum of photon of energy 3 mev in kg ms-1?
Which of the following is/are true for cathode ray
- Calculate the frequency of a photon of energy 6.5 × 10−19 J.
- Can this photon cause the emission of an electron from the surface of Cs of work function 2.14 eV? If yes, what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron?
