Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(i) A ray of light incident on face AB of an equilateral glass prism, shows minimum deviation of 30°. Calculate the speed of light through the prism.
(ii) Find the angle of incidence at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC.
Solution
(i) μ = `sin((A + δ_m)/2)/(sin(A/2))`
= `(sin((60 + 30)/2))/(sin(60^circ/2))`
= `sqrt(2)`
Also μ = `c/v`
⇒ v = `(3 xx 10^8)/sqrt(2)` m/s
(ii)
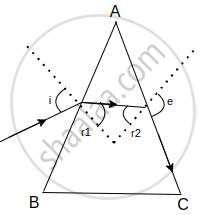
At face AC, let the angle of incidence be r2. For grazing ray, e = 90°
⇒ μ = `1/sinr_2`
⇒ r2 = `sin^-1(1/sqrt(2))` = 45°
Let the angle of refraction at face AB be r1.
Now r1 + r2 = A
∴ r1 = A – r2 = 60º – 45º = 15º
Let the angle of incidence at this face be i
μ = `sini/sin r_1`
⇒ `sqrt(2) = sini/sin15^circ`
∴ i = `sin^-1 (sqrt(2).sin15^circ)` = 21.5º
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The photoelectric threshold wavelength of a metal is 230 nm. Determine the maximum kinetic energy in joule and in eV of the ejects electron for the metal surface when it is exposed to a radiation of wavelength 180 nm.
[Planck’s constant : h = 6.63 * 10-34 Js, Velocity of light : C = 3 * 108 m/s.]
Find the wave number of a photon having energy of 2.072 eV
Given : Charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19 C,
Velocity of light in air = 3 x 108 m/s,
Planck’s constant = 6.63 x 10-34 J-s.
The work function for a metal surface is 2.2eV. If the light of wavelength 5000Å is incident on the surface of the metal, find the threshold frequency and incident frequency. Will there be an emission of photoelectrons or not? (c = 3 x 108 m/ s, 1eV = 1.6x10-19 J , h = 6.63 x 10-34 J.s.)
According to Einstein’s model minimum energy needed for the electron to escape from a metal surface having work function ϕ0, the electron is emitted with maximum kinetic energy, Kmax = ______.
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted by a metal (work function = 1.5 eV) when it is illuminated with light of wavelength 198 nm.
Plot a labelled graph of |Vs| where Vs is stopping potential versus frequency f of the incident radiation. State how will you use this graph to determine the value of Planck's constant?
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is double the stopping potential will
What will be wavelength of a photon of momentum 6.6 × 10–24 kgms–1?
- Calculate the energy and momentum of a photon in a monochromatic beam of wavelength 331.5 nm.
- How fast should a hydrogen atom travel in order to have the same momentum as that of the photon in part (a)?
How does stopping potential in photoelectric emission vary if the frequency of incident radiation decreases?
