Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write two points of difference between an interference pattern and a diffraction pattern.
Solution
- The interference pattern has a number of equally spaced bright and dark bands. The diffraction pattern has a central bright maximum which is twice as wide as the other maxima. The intensity falls as we go to successive maxima away from the centre, on either side.
- We calculate the interference pattern by superposing two waves originating from the two narrow slits. The diffraction pattern is a superposition of a continuous family of waves originating from each point on a single slit.
RELATED QUESTIONS
A point is situated at 7cm and 7·2 cm from two coherent sources. Find the· nature of illumination at the point if wavelength of light is 4000A.
Two wavelengths of sodium light of 590 nm and 596 nm are used in turn to study the diffraction taking place at a single slit of aperture 2 × 10−6 m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1·5 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
In Fraunhofer diffraction, how is the angular width of the central bright fringe affected when slit separation is increased?
Show graphically the intensity distribution in Fraunhofer's single slit diffraction experiment. Label the axes.
Two wavelengths of sodium light 590 nm and 596 nm are used, in turn, to study the diffraction taking place due to a single slit of aperture 1 × 10−4 m. The distance between the slit and the screen is 1.8 m. Calculate the separation between the positions of the first maxima of the diffraction pattern obtained in the two cases.
Diffraction effects are easy to notice in the case of sound waves than in case of light waves because
Which of the following device is used to study the spectra of light?
Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of the hole is increased ______.
- the size decreases.
- the intensity increases.
- the size increases.
- the intensity decreases.
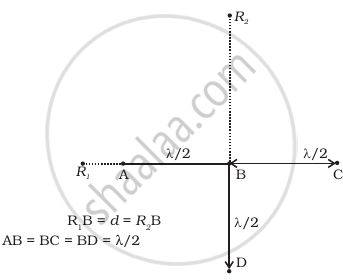
Four identical monochromatic sources A, B, C, D as shown in the (Figure) produce waves of the same wavelength λ and are coherent. Two receiver R1 and R2 are at great but equal distances from B.
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when B is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when D is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources B or D has been turned off?
In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit, how will the angular width of the central maximum change, if the screen is moved closer to the slit?
Justify your answer.
