Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ray PQ is incident normally on the face AB of a triangular prism of refracting angle 60° as shown in figure. The prism is made of a transparent material of refractive index
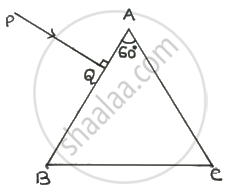
Solution
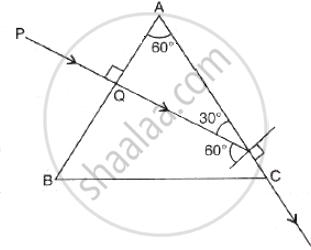
Given: ∠A = 60°, ∠i = 0°
At M: Sin C =
∴ C = 60°
So the ray PM after refraction from the face AC grazes along AC.
∴ ∠C = 90°
From ∠i + ∠C = ∠A + ∠δ
Or 0° + 90° = 60° + ∠δ
∴ δ = 90° – 60° = 30°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A ray of light passing from air through an equilateral glass prism undergoes minimum deviation when the angle of incidence is 3/4 th of the angle of prism. Calculate the speed of light in the prism.
Find the angle of incidence at face AB so that the emergent ray grazes along the face AC.
Write the relationship between angle of incidence ‘i’, angle of prism ‘A’ and angle of minimum deviations for a triangular prism.
Trace the path of the ray (P) of light passing through the glass prism as shown in the figure. The prism is made of glass with critical angle ic = 41°.
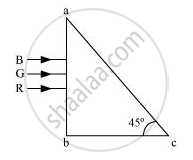
Three light rays red (R), green (G) and blue (B) are incident on a right angled prism ‘abc’ at face ‘ab’. The refractive indices of the material of the prism for red, green and blue wavelengths are 1.39, 1.44 and 1.47 respectively. Out of the three which colour ray will emerge out of face ‘ac’? Justify your answer. Trace the path of these rays after passing through face ‘ab’.
Can you ever have a situation in which a light ray goes undeviated through a prism?
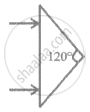
An isosceles prism of angle 120° has a refractive index 1.44. Two parallel monochromatic rays enter the prism parallel to each other in air as shown. The rays emerge from the opposite faces:
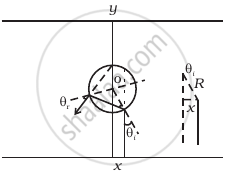
An infinitely long cylinder of radius R is made of an unusual exotic material with refractive index –1 (Figure). The cylinder is placed between two planes whose normals are along the y direction. The center of the cylinder O lies along the y-axis. A narrow laser beam is directed along the y direction from the lower plate. The laser source is at a horizontal distance x from the diameter in the y direction. Find the range of x such that light emitted from the lower plane does not reach the upper plane.
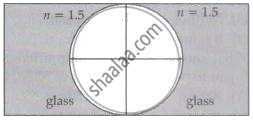
Two concave refracting surfaces of equal radii of curvature face each other in the air as shown in the figure. The point object O is placed midway between the centre and one of the poles. Then the separation between the images of O formed by each refracting surface is ______.
A ray of monochromatic light passes through an equilateral glass prism in such a way that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence and each of these angles is 3/4 times the angle of the prism. Determine the angle of deviation and the refractive index of the glass prism.
