Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
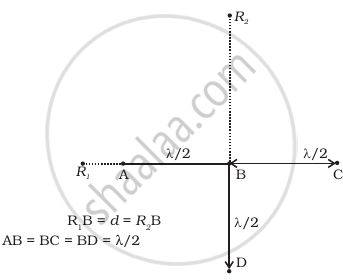
Four identical monochromatic sources A, B, C, D as shown in the (Figure) produce waves of the same wavelength λ and are coherent. Two receiver R1 and R2 are at great but equal distances from B.
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when B is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers picks up the larger signal when D is turned off?
- Which of the two receivers can distinguish which of the sources B or D has been turned off?
Solution
i. Consider the disturbances at R1 which is a distance d from A. Let the wave at R1 because of A be YA = a cos ωt. The path difference of the signal from A with that from B is λ/2 and hence the phase difference is π.
Thus the wave at R1 because of B is `y_B = a cos (ωt - π) = - a cos ωt)`
The path difference of the signal from C with that from A is λ and hence the phase difference is 2π.
Thus the wave at R1 because of C is yc = a cos ωt.
The path difference between the signal from D with that of A is `sqrt(d^2 + (lambda/2)^2) - (d - lambda/2)`
= `d(1 + lambda/(4d^2))^(1/2) - d + lambda/2`
= `d(1 + lambda^2/(8d^2))^(1/2) - d + lambda/2`
If d >>λ the path difference `∼ λ/2` and hence the phase difference is π.
∴ `y_D = - a cos ωt`
Thus, the signal picked up at R1 is `y_A + y_B + y_C + y_D` = 0
Let the signal picked up at R2 from B be `y_B = a_1 cos ωt`
The path difference between signal at D and that at B is λ/2.
∴ `y_D = - a_1 cos ωt`
The path difference between signal at A and that at B is `sqrt((d)^2 + (lambda/2)^2) - d = d(1 + lambda^2/(4d^2))^(1/2) - d ∼ 1/8 lambda^2/d^2`
∴ The phase difference is `(2pi)/(8λ) * λ^2/d^2 = (piλ)/(4d) = phi ∼ 0`.
Hence, `y_A = a_1 cos (ωt - phi)`
Similarly, `y_C = a_1 cos (ωt - phi)`
∴ Signal picked up by R2 is `y_A + y_B + y_C + y_D = y = 2a_1 cos (ωt - phi)`
∴ `|y|^2 = 4a_1^2 cos^2 (ωt - phi)`
∴ `<I> = 2a_1^2`
Thus R1 picks up the larger signal.
ii. If B is switched off
R1 picks up y = a cos ωt
∴ `<I_(R_1)> = 1/2 a^2`
R2 picks up y = a cos ωt
∴ `<I_(R_2)> = 1/2 a_1^2`
Thus R1 and R2 pick up the same signal.
iii. If D is switched off
R1 picks up y = a cos ω t
∴ `<I_(R_1)> = 1/2 a^2`
R2 picks up y = 3a cos ωt
∴ `<I_(R_2)> = 1/2 9a^2`
Thus R2 picks up a larger signal compared to R1.
iv. Thus a signal at R1 indicates B has been switched off and an enhanced signal at R2 indicates D has been switched off.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width 'd' with incident light of wavelength 'λ', at an angle of diffraction θ. the condition for first minimum is ....
(a)`lambda sin theta =d`
(b) `d costheta =lambda`
(c)`d sintheta=lambda`
(d) `lambda cos theta=d`
In a single slit diffraction experiment, how does the angular width of the central maxima change when:
- screen is moved away from the plane of the slit?
- width of the slit is increased?
- light of larger wavelength is used?
What should be the order of obstacle or aperture for diffraction of light?
Wavelength of light of frequency 100 Hz is
Write two points of difference between an interference pattern and a diffraction pattern.
How can you differentiate whether a pattern is produced by a single slit or double slit?
In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit, how will the angular width of the central maximum change, if orange light is used in place of green light?
Justify your answer.
In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit, how will the angular width of the central maximum change, if the screen is moved closer to the slit?
Justify your answer.
In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit, how will the angular width of the central maximum change, if the slit width is decreased?
Justify your answer.
Draw a labelled graph showing the variation in intensity of diffracted light with diffracting angle in a single slit Fraunhofer diffraction experiment.
