Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A simple motor is made in a school laboratory. A coil of wire is mounted on an axle between the poles of a horseshoe magnet, as illustrated.
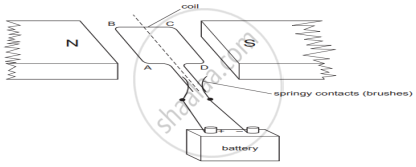
In the example above, coil ABCD is horizontal and the battery is connected as shown.
- For this position, state the direction of the force on the arm AB.
- Why does the current in the arm BC not contribute to the turning force on the coil?
उत्तर
- downwards
- Because BC is in the same direction as the direction of field lines. Force is minimum when the direction of current in the conductor is the same as that of the magnetic field. BC will not contribute as the force on this part of the coil will be cancelled by the force on DA.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Name the rule for finding the direction of magnetic field produced by a straight current-carrying conductor.
What is the shape of a current-carrying conductor whose magnetic field pattern resembles that of a bar magnet?
The magnetic field lines in the middle of the current-carrying solenoid are?
(a) circles
(b) spirals
(c) parallel to the axis of the tube
(d) perpendicular to the axis of the tube
The magnetic field associated with a current-carrying straight conductor is in anticlockwise direction. If the conductor was held along the east-west direction, what will be the direction of current through it? Name and state the rule applied to determine the direction of current?
State condition when magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is zero?
State under what conditions force acting on a current carrying conductor which is freely suspended in a magnetic field can be maximum.
What do you know about Michael Faraday?
|
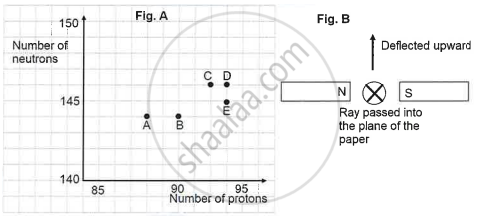
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Name the law used to identify the radioactive radiation emitted by the element.