Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A square coil of side 10 cm consists of 20 turns and carries a current of 12 A. The coil is suspended vertically and the normal to the plane of the coil makes an angle of 30° with the direction of a uniform horizontal magnetic field of magnitude 0.80 T. What is the magnitude of torque experienced by the coil?
उत्तर
Length of a side of the square coil, l = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Current flowing in the coil, I = 12 A
Number of turns on the coil, n = 20
Angle made by the plane of the coil with the magnetic field, θ = 30°
Strength of magnetic field, B = 0.80 T
Magnitude of the magnetic torque experienced by the coil in the magnetic field is given by the relation,
τ = n BIA sin θ
Where,
A = Area of the square coil
= l × l
= 0.1 × 0.1
= 0.01 m2
∴ τ = 20 × 0.8 × 12 × 0.01 × sin 30°
= 0.96 N m
Hence, the magnitude of the torque experienced by the coil is 0.96 N m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a chamber, a uniform magnetic field of 6.5 G (1 G = 10–4 T) is maintained. An electron is shot into the field with a speed of 4.8 × 106 m s−1 normal to the field. Explain why the path of the electron is a circle. Determine the radius of the circular orbit. (e = 1.5 × 10–19 C, me = 9.1 × 10–31 kg)
A rectangular loop of wire of size 4 cm × 10 cm carries a steady current of 2 A. A straight long wire carrying 5 A current is kept near the loop as shown. If the loop and the wire are coplanar, find
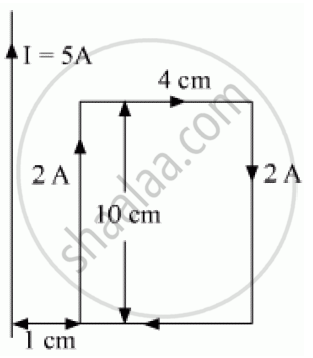
(i) the torque acting on the loop and
(ii) the magnitude and direction of the force on the loop due to the current carrying wire.
A rectangular loop of wire of size 2 cm × 5 cm carries a steady current of 1 A. A straight long wire carrying 4 A current is kept near the loop as shown. If the loop and the wire are coplanar, find (i) the torque acting on the loop and (ii) the magnitude and direction of the force on the loop due to the current carrying wire.

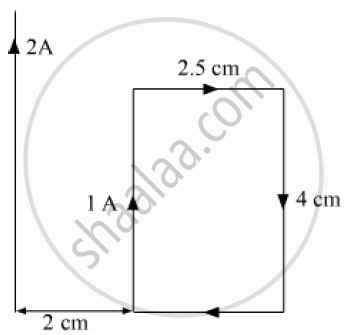
A rectangular loop of wire of size 2.5 cm × 4 cm carries a steady current of 1 A. A straight wire carrying 2 A current is kept near the loop as shown. If the loop and the wire are coplanar, find the (i) torque acting on the loop and (ii) the magnitude and direction of the force on the loop due to the current carrying wire.
A rectangular loop of size l × b carrying a steady current I is placed in a uniform magnetic field `vecB`. Prove that the torque `vectau`acting on the loop is give by `vectau =vecm xx vecB,`where `vecm` is the magnetic moment of the loop.
A magnetised needle of magnetic moment 4.8 × 10−2 JT−1 is placed at 30° with the direction of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3 × 10−2 T. Calculate the torque acting on the needle.
The rectangular wire-frame, shown in figure, has a width d, mass m, resistance R and a large length. A uniform magnetic field B exists to the left of the frame. A constant force F starts pushing the frame into the magnetic field at t = 0. (a) Find the acceleration of the frame when its speed has increased to v. (b) Show that after some time the frame will move with a constant velocity till the whole frame enters into the magnetic field. Find this velocity v0. (c) Show that the velocity at time t is given by
v = v0(1 − e−Ft/mv0).
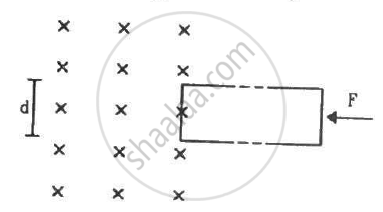
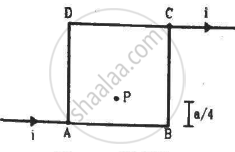
Figure shows a square loop of edge a made of a uniform wire. A current i enters the loop at the point A and leaves it at the point C. Find the magnetic field at the point P which is on the perpendicular bisector of AB at a distance a/4 from it.
Find the magnetic field B at the centre of a rectangular loop of length l and width b, carrying a current i.
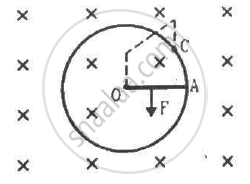
Figure shows a conducting circular loop of radius a placed in a uniform, perpendicular magnetic field B. A thick metal rod OA is pivoted at the centre O. The other end of the rod touches the loop at A. The centre O and a fixed point C on the loop are connected by a wire OC of resistance R. A force is applied at the middle point of the rod OAperpendicularly, so that the rod rotates clockwise at a uniform angular velocity ω. Find the force.
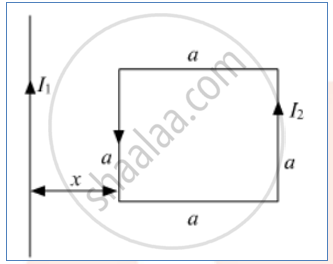
A square loop of side 'a' carrying a current I2 is kept at distance x from an infinitely long straight wire carrying a current I1 as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the resultant force acting on the loop.
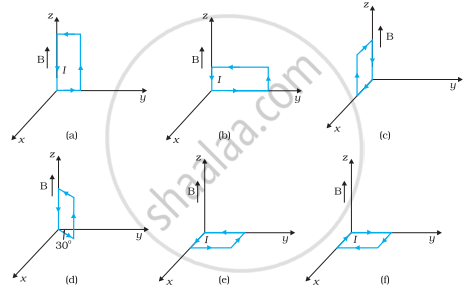
A uniform magnetic field of 3000 G is established along the positive z-direction. A rectangular loop of sides 10 cm and 5 cm carries a current of 12 A. What is the torque on the loop in the different cases shown in fig.? What is the force on each case? Which case corresponds to stable equilibrium?
Consider the motion of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field directed into the paper. If velocity v of the particle is in the plane of the paper the charged particle will ______.
A rectangular conducting loop consists of two wires on two opposite sides of length l joined together by rods of length d. The wires are each of the same material but with cross-sections differing by a factor of 2. The thicker wire has a resistance R and the rods are of low resistance, which in turn are connected to a constant voltage source V0. The loop is placed in uniform a magnetic field B at 45° to its plane. Find τ, the torque exerted by the magnetic field on the loop about an axis through the centres of rods.
- Assertion (A): The deflecting torque acting on a current-carrying loop is zero when its plane is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
- Reason (R): The deflecting torque acting on a loop of the magnetic moment `vecm` in a magnetic field `vecB` is given by the dot product of `vecm` and `vecB`.
