Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end?
उत्तर १
Mass of the string, M = 2.50 kg
Tension in the string, T = 200 N
Length of the string, l = 20.0 m
Mass per unit length, `mu = M/l = 2.50/20 = 0.125 "kg m"^(-1)`
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation:
`v = sqrt(T/mu)`
`= sqrt(200/0.125) = sqrt(1600)` = 40 m/s
∴Time taken by the disturbance to reach the other end, `t = l/v = 20/40 = 0.50 s`
उत्तर २
Tension,T = 200 N
Length l = 20.0 m , Mass M = 2.50 kg
Mass per unit length, mu = `2.50/20.0 kg m^(-1) = 0.125 kg m^(-1)`
Wave velocity, `v = sqrt(T/mu) = sqrt(200 N)/(0.125 kg m^(-1))`
or `v = sqrt(1600) ms^(-1) = 40 ms^(-1)`
`Time t = l/v = 20.0/40 s = 1/2 s = 0.5 s`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a transverse wave on a string is reflected from the free end, the phase change produced is ..............
(a) zero rad
(b) ` pi/2 ` rad
(c) `(3pi)/4` rad
(d) `pi` rad
Explain the reflection of transverse and longitudinal waves from a denser medium and a rared medium.
A mechanical wave propagates in a medium along the X-axis. The particles of the medium
(a) must move on the X-axis
(b) must move on the Y-axis
(c) may move on the X-axis
(d) may move on the Y-axis.
A particle on a stretched string supporting a travelling wave, takes 5⋅0 ms to move from its mean position to the extreme position. The distance between two consecutive particles, which are at their mean positions, is 2⋅0 cm. Find the frequency, the wavelength and the wave speed.
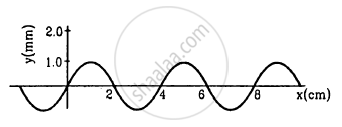
Figure shows a plot of the transverse displacements of the particles of a string at t = 0 through which a travelling wave is passing in the positive x-direction. The wave speed is 20 cm s−1. Find (a) the amplitude, (b) the wavelength, (c) the wave number and (d) the frequency of the wave.
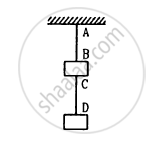
Two blocks each having a mass of 3⋅2 kg are connected by a wire CD and the system is suspended from the ceiling by another wire AB (See following figure). The linear mass density of the wire AB is 10 g m−1 and that of CD is 8 g m−1. Find the speed of a transverse wave pulse produced in AB and CD.
An organ pipe, open at both ends, contains
A circular loop of string rotates about its axis on a frictionless horizontal place at a uniform rate so that the tangential speed of any particle of the string is ν. If a small transverse disturbance is produced at a point of the loop, with what speed (relative to the string) will this disturbance travel on the string?
A transverse wave of amplitude 0⋅50 mm and frequency 100 Hz is produced on a wire stretched to a tension of 100 N. If the wave speed is 100 m s−1, what average power is the source transmitting to the wire?
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
`"y" = 2sqrt(x - "vt")`
