Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A string of mass 2.50 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, how long does the disturbance take to reach the other end?
Solution 1
Mass of the string, M = 2.50 kg
Tension in the string, T = 200 N
Length of the string, l = 20.0 m
Mass per unit length, `mu = M/l = 2.50/20 = 0.125 "kg m"^(-1)`
The velocity (v) of the transverse wave in the string is given by the relation:
`v = sqrt(T/mu)`
`= sqrt(200/0.125) = sqrt(1600)` = 40 m/s
∴Time taken by the disturbance to reach the other end, `t = l/v = 20/40 = 0.50 s`
Solution 2
Tension,T = 200 N
Length l = 20.0 m , Mass M = 2.50 kg
Mass per unit length, mu = `2.50/20.0 kg m^(-1) = 0.125 kg m^(-1)`
Wave velocity, `v = sqrt(T/mu) = sqrt(200 N)/(0.125 kg m^(-1))`
or `v = sqrt(1600) ms^(-1) = 40 ms^(-1)`
`Time t = l/v = 20.0/40 s = 1/2 s = 0.5 s`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain why (or how) Solids can support both longitudinal and transverse waves, but only longitudinal waves can propagate in gases
Explain the reflection of transverse and longitudinal waves from a denser medium and a rared medium.
A wave going in a solid
(a) must be longitudinal
(b) may be longitudinal
(c) must be transverse
(d) may be transverse.
Mark out the correct options.
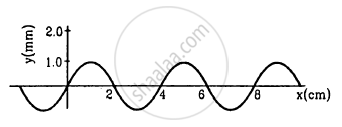
Figure shows a plot of the transverse displacements of the particles of a string at t = 0 through which a travelling wave is passing in the positive x-direction. The wave speed is 20 cm s−1. Find (a) the amplitude, (b) the wavelength, (c) the wave number and (d) the frequency of the wave.
A steel wire of length 64 cm weighs 5 g. If it is stretched by a force of 8 N, what would be the speed of a transverse wave passing on it?
Two wires of different densities but same area of cross section are soldered together at one end and are stretched to a tension T. The velocity of a transverse wave in the first wire is double of that in the second wire. Find the ratio of the density of the first wire to that of the second wire.
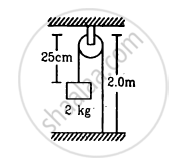
In the arrangement shown in figure , the string has a mass of 4⋅5 g. How much time will it take for a transverse disturbance produced at the floor to reach the pulley? Take g = 10 m s−2.
A 660 Hz tuning fork sets up vibration in a string clamped at both ends. The wave speed for a transverse wave on this string is 220 m s−1 and the string vibrates in three loops. (a) Find the length of the string. (b) If the maximum amplitude of a particle is 0⋅5 cm, write a suitable equation describing the motion.
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 2 cos (3x) sin (10t)
