Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
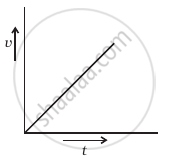
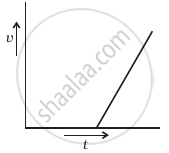
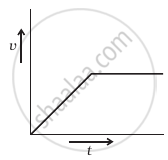
A tall cylinder is filled with viscous oil. A round pebble is dropped from the top with zero initial velocity. From the plot shown in figure, indicate the one that represents the velocity (v) of the pebble as a function of time (t).
पर्याय
उत्तर
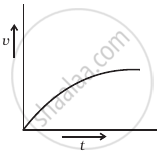
Explanation:
In fluids, when the pebble is dropped from the top of a tall cylinder filled with viscous oil, a variable force called viscous force will act which increases with an increase in speed. And at equilibrium this velocity becomes constant, that constant velocity is called terminal velocity.
When the pebble is falling through the viscous oil, the viscous force is F = 6πηrv
Where r is the radius of the pebble, v is instantaneous speed, η is the coefficient of viscosity. As the force is variable, hence acceleration is also variable so the v-t graph will not be a straight line. First velocity increases and then becomes constant known as terminal velocity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A piece of wood is taken deep inside a long column of water and released. It will move up
A solid sphere falls with a terminal velocity of 20 m s−1 in air. If it is allowed to fall in vacuum,
A solid sphere moves at a terminal velocity of 20 m s−1 in air at a place where g = 9.8 m s−2. The sphere is taken in a gravity-free hall having air at the same pressure and pushed down at a speed of 20 m s−1.
(a) Its initial acceleration will be 9.8 m s−2 downward.
(b) It initial acceleration will be 9.8 m s−2 upward.
(c) The magnitude of acceleration will decrease as the time passes.
(d) It will eventually stop
Two spheres of equal masses but radii r1 and r2 are allowed to fall in a liquid of infinite column. The ratio of their terminal velocities are ____________.
A small sphere of mass m is dropped from a great height. After it has fallen 100 m, it has attained its terminal velocity and continues to fall at that speed. The work done by air friction against the sphere during the first 100 m of fall is ______.
Two small spherical metal balls, having equal masses, are made from materials of densities `rho_1` and`rho_2 (rho_1 = 8rho_2)` and have radii of 1 mm and 2 mm, respectively, they are made to fall vertically (from rest) in a viscous medium whose coefficient of viscosity equals `eta` and whose density is `0.1rho_2` The ratio of their terminal velocities would be, ____________.
Two rain drops falling through air have radii in the ratio 1 : 2. They will have terminal velocity in the ratio ______.
A small spherical ball of radius 0.1 mm and density 104 kg m-3 falls freely under gravity through a distance of h before entering a tank of water. If, after entering the water the velocity of the ball does not change and it continues to fall with the same constant velocity inside the water, then the value of h will be ______ m.
(Given g = 10 ms-2, the viscosity of water = 1.0 × 10-5 N-sm-2).
A spherical solid ball of volume V is made up of a material of density ρ1. It is falling through the liquid of density ρ2(ρ2 < ρ1). Assume that, the liquid applies a viscous force on the ball that is proportional to the square of the speed vt, i.e., `["F"_"viscous" = "KV"_"t"^2]`, then the terminal speed of the ball is ______.
(g = acceleration due to gravity)
Two equal drops of water are falling through air with a steady velocity v. If the drops coalesce, the new velocity will be ______.