Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
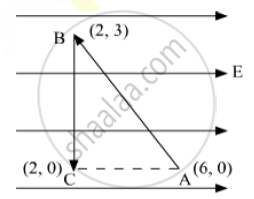
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C. (ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
उत्तर
Since work done is independent of the path therefore we may directly move from A to C. Potential difference between A and C,
`V_c -V_A = -int_A^C vecE *vecdl`
= `int_A^C Edl cos 180°`
=` - E (-1)int_A^Cdl`
= `E xx 4`
= 4E
So, VC − VA = 4E
(ii) Electric potential will be more at point C as direction of electric field is in decreasing potential. Hence
VC > VA
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the principle of a device that can build up high voltages of the order of a few million volts.
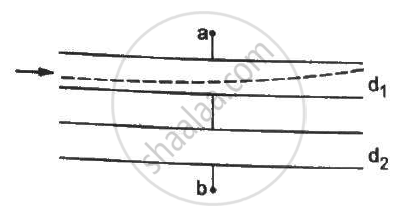
Both the capacitors shown in figure are made of square plates of edge a. The separations between the plates of the capacitors are d1 and d2 as shown in the figure. A potential difference V is applied between the points a and b. An electron is projected between the plates of the upper capacitor along the central line. With what minimum speed should the electron be projected so that it does not collide with any plate? Consider only the electric forces.
Find the potential difference between the points A and B and between the points B and C of the figure in steady state.

A charge of `+2.0 xx 10^-8 C` is placed on the positive plate and a charge of `-1.0 xx 10^-8 C` on the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance `1.2 xx 10^-3 "uF"` . Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
A charge of 1 µC is given to one plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 0⋅1 µF and a charge of 2 µC is given to the other plate. Find the potential difference developed between the plates.
In circuits, a difference in potential from one point to another is often called ______.
The unit of potential difference as used in electrical circuits is ________.
Two metal pieces having a potential difference of 800 V are 0.02 m apart horizontally. A particle of mass 1.96 × 10–15 kg is suspended in equilibrium between the plates. If e is the elementary charge, then charge on the particle is ______.
- It depends only on the initial and final position.
- It is the work done per unit positive charge in moving from one point to other.
- It is more for a positive charge of two units as compared to a positive charge of one unit.
Work done in moving a unit positive charge through a distance of x meter on an equipotential surface is:-
