Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
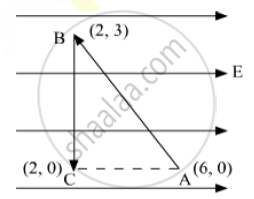
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C. (ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
उत्तर
Since work done is independent of the path therefore we may directly move from A to C. Potential difference between A and C,
`V_c -V_A = -int_A^C vecE *vecdl`
= `int_A^C Edl cos 180°`
=` - E (-1)int_A^Cdl`
= `E xx 4`
= 4E
So, VC − VA = 4E
(ii) Electric potential will be more at point C as direction of electric field is in decreasing potential. Hence
VC > VA
संबंधित प्रश्न
Distinguish between Conductors and Insulators.
Draw a labelled diagram of Van de Graaff generator. State its working principle to show how by introducing a small charged sphere into a larger sphere, a large amount of charge can be transferred to the outer sphere. State the use of this machine and also point out its limitations.
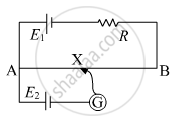
In the circuit diagram given below, AB is a uniform wire of resistance 15 Ω and length 1 m. It is connected to a cell E1 of emf 2V and negligible internal resistance and a resistance R. The balance point with another cell E2 of emf 75 mV is found at 30 cm from end A. Calculate the value of R.
Is there any restriction on the upper limit of the high voltage set up in Van de Graff generator machine? Explain.
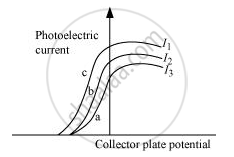
The figure shows a plot of three curves a, b, c, showing the variation of photocurrent vs collector plate potential for three different intensities I1, I2and I3 having frequencies v1, v2 and v3 respectively incident of a photosensitive surface.
Point out the two curves for which the incident radiations have same frequency but different intensities.
Find the potential difference between the points A and B and between the points B and C of the figure in steady state.

The unit of potential difference as used in electrical circuits is ________.
Assertion: Electric potential and electric potential energy are different quantities.
Reason: For a system of positive test charge and point charge electric potential energy = electric potential.
On moving a charge of Q coulomb by X cm, W J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is ______.
An α-particle and a proton are accelerate at same potential difference from rest. What will be the ratio of their final velocity?
