Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A thin converging lens is formed with one surface convex and the other plane. Does the position of image depend on whether the convex surface or the plane surface faces the object?
उत्तर
Yes. Using the lens maker formula we can show it. We know that the formula is:
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right)\]
Where, f is the focal length of the thin converging lens.
μ2 and μ1 are refractive indexes of lens and air respectively.
R1 and R2 are the radius of curvature of convex and plane surfaces respectively.
Here, R2 = ∞ because of the plane surface.
Case 1
When the convex surface is facing the object, we have:
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{\infty} \right)\]
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\frac{1}{R_1} . . . (i)\]
Case 2
When the plane surface is facing the object, we have:
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\left( \frac{1}{\infty} - \frac{1}{-R_1} \right)\]
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\frac{1}{R_1} . . . (ii)\]
For Case 1, the focal length is positive and for the Case 2 the focal length is positive. Thus, the image distance is same in both cases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50 cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens if the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens.
Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2m.
(a) At what distance should the lens be held from the figure in order to view the squares distinctly with the maximum possible magnifying power?
(b) What is the magnification in this case?
(c) Is the magnification equal to the magnifying power in this case? Explain.

Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
The focal length of a lens is +150 mm. What kind of lens is it and what is its power?
Define the term power of a lens.
How does focal length of a lens change when red light incident on it is replaced by violet light? Give reason for your answer.
Find the radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens, whose focal length is 0.3 m and the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
A double convex lens has focal length 25 cm. The radius of curvature of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
What is meant by the power of accommodation produced?
How is accommodation produced?
The following diagram shows the object O and the image I formed by a lens. Copy the diagram and on it mark the positions of the lens LL’ and focus (F). Name the lens.
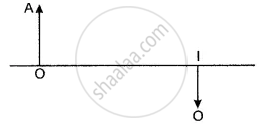
If the lens is of focal length 25 cm. Calculate the power of the lens.
If there is a convex lens of focal length 75 cm and a concave lens of focal length 40 cm, then calculate their combined power and combined focal length.
The focal length of a concave lens is 20 cm. The focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm. These two are placed in contact with each other. What is the power of the combination? Is it diverging, converging or undeviating in nature?
A point object is placed at O in front of a glass sphere as shown in figure.
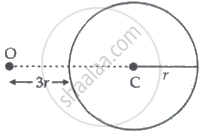
Show the formation of the image by the sphere.
An object is kept at a distance of 1m from a lens of power +2D:
- Identify the type of lens.
- Calculate its focal length and distance of the image formed.
In what unit is the power of a lens expressed?
