Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A thin converging lens is formed with one surface convex and the other plane. Does the position of image depend on whether the convex surface or the plane surface faces the object?
Solution
Yes. Using the lens maker formula we can show it. We know that the formula is:
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{R_2} \right)\]
Where, f is the focal length of the thin converging lens.
μ2 and μ1 are refractive indexes of lens and air respectively.
R1 and R2 are the radius of curvature of convex and plane surfaces respectively.
Here, R2 = ∞ because of the plane surface.
Case 1
When the convex surface is facing the object, we have:
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\left( \frac{1}{R_1} - \frac{1}{\infty} \right)\]
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\frac{1}{R_1} . . . (i)\]
Case 2
When the plane surface is facing the object, we have:
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\left( \frac{1}{\infty} - \frac{1}{-R_1} \right)\]
\[\frac{1}{f} = \left( \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1} - 1 \right)\frac{1}{R_1} . . . (ii)\]
For Case 1, the focal length is positive and for the Case 2 the focal length is positive. Thus, the image distance is same in both cases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens.
A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses.
Which of the two has a greater power: a lens of short focal length or a lens of large focal length?
What is the power of a convex lens lens whose focal length is 80 cm?
What is the nature of a lens whose power is, −4 D?
A lens has a focal length of, −10 cm. What is the power of the lens and what is its nature?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
For converging lenses, the power is __________ while for diverging lenses, the power is ___________.
A convex lens of power 5 D and a concave lens of power 7.5 D are placed in contact with each other. What is the :
(a) power of this combination of lenses?
(b) focal length of this combination of lenses?
The power of a combination of two lenses X and Y is 5 D. If the focal length of lens X be 15 cm :
(a) calculate the focal length of lens Y.
(b) state the nature of lens Y.
How does the power of a lens change if its focal length is doubled?
On reducing the focal length of a lens, its power ______.
Name the type of lens whose power is positive.
The image of an object formed by a lens is real, inverted and of the same size as the object. If the image is at a distance of 40 cm from the lens, what is the nature and power of the lens ? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation `1/f =1/f_1 +1/f_2`for two thin lenses kept in contact coaxially.
Find the radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens, whose focal length is 0.3 m and the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
Consider three converging lenses L1, L2 and L3 having identical geometrical construction. The index of refraction of L1 and L2 are \[\mu_1 \text{ and } \mu_2\] respectively. The upper half of the lens L3 has a refractive index \[\mu_1\] and the lower half has \[\mu_2\] following figure . A point object O is imaged at O1 by the lens L1 and at O2 by the lens L2placed in same position. If L3 is placed at the same place,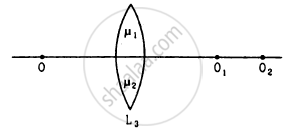
(a) there will be an image at O1
(b) there will be an image at O2.
(c) the only image will form somewhere between O1 and O2
(d) the only image will form away from O2.
A 5.0 diopter lens forms a virtual image which is 4 times the object placed perpendicularly on the principal axis of the lens. Find the distance of the object from the lens.
Surabhi from std. X uses spectacle. The power of the lenses in her spectacle is 0.5 D.
Answer the following questions from the given information:
- Identify the type of lenses used in her spectacle.
- Identify the defect of vision Surabhi is suffering from.
- Find the focal length of the lenses used in her spectacle.
A convex lens is of focal length 20 cm. Find its power.
