Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A water particle of mass 10.0 mg and with a charge of 1.50 × 10−6 C stays suspended in a room. What is the magnitude of electric field in the room? What is its direction ?
उत्तर
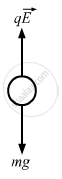
Mass of the particle,
\[m = 10 \text{mg } = 10 \times {10}^{- 5} \] kg
Charge on the particle,
\[q = 1 . 5 \times {10}^{- 6} C\]
Let the magnitude of the electric field be E.
The particle stays suspended. Therefore,
Downward gravitational force = Upward electric force
That is, mg = qE
\[\Rightarrow E = \frac{mg}{q} = \frac{10 \times {10}^{- 5} \times 10}{1 . 5 \times {10}^{- 6}}\]
\[ = \frac{1000}{15} = 66 . 7 \] N/C
The direction of the electric field will be upward to balance the downward gravitational force.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
- Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centers separated by a distance of 50 cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is 6.5 × 10−7 C? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation.
- What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double the above amount, and the distance between them is halved?
Write any two important points of similarities and differences each between Coulomb's law for the electrostatic field and Biot-Savart's law of the magnetic field ?
A charge of 1.0 C is placed at the top of your college building and another equal charge at the top of your house. Take the separation between the two charges to be 2.0 km. Find the force exerted by the charges on each other. How many times your weight is this force?
Suppose all the electrons of 100 g water are lumped together to form a negatively-charged particle and all the nuclei are lumped together to form a positively-charged particle. If these two particles are placed 10.0 cm away from each other, find the force of attraction between them. Compare it with your weight.
Four equal charges of 2.0 × 10−6 C each are fixed at the four corners of a square of side 5 cm. Find the Coulomb's force experienced by one of the charges due to the other three.
A hydrogen atom contains one proton and one electron. It may be assumed that the electron revolves in a circle of radius 0.53 angstrom (1 angstrom = 10−10 m and is abbreviated as Å ) with the proton at the centre. The hydrogen atom is said to be in the ground state in this case. Find the magnitude of the electric force between the proton and the electron of a hydrogen atom in its ground state.
Two small spheres, each with a mass of 20 g, are suspended from a common point by two insulating strings of length 40 cm each. The spheres are identically charged and the separation between the balls at equilibrium is found to be 4 cm. Find the charge on each sphere.
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C and a mass of 100 g is placed at the bottom of a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30°. Where should another particle B, with the same charge and mass, be placed on the incline so that it may remain in equilibrium?
A point charge produces an electric field of magnitude 5.0 NC−1 at a distance of 40 cm from it. What is the magnitude of the charge?
Two equal charges, 2.0 × 10−7 C each, are held fixed at a separation of 20 cm. A third charge of equal magnitude is placed midway between the two charges. It is now moved to a point 20 cm from both the charges. How much work is done by the electric field during the process?
Solve numerical example.
Three equal charges of 10×10-8 C respectively, each located at the corners of a right triangle whose sides are 15 cm, 20 cm, and 25cm respectively. Find the force exerted on the charge located at the 90° angle.
Three charges +Q, q, +Q are placed respectively, at distance, 0, d/2 and d from the origin, on the X-axis. If the net force experienced by +Q, placed at x = 0, is zero then value of q is ____________.
A force F acts between sodium and chlorine ions of salt (sodium chloride) when put 1 cm apart in air. The permittivity of air and dielectric constant of water are `epsilon_0` and K respectively. When a piece of salt is put in water, electrical force acting between sodium and chlorine ions 1 cm apart is ____________.
Polarised dielectric is equivalent to ______.
For charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance R the magnitude of the electrostatic force is given by ______.
Two identical thin rings, each of radius a meter, are coaxially placed at a distance R meter apart. If Q1 coulomb and Q2 coulomb are respectively the charges uniformly spread on the two rings, the work done in moving a charge q coulomb from the centre of one ring to that of the other is ______.
A charge Q is divided into two parts of q and Q – q. If the coulomb repulsion between them when they are separated is to be maximum, the ratio of Q/q should be ______.
A spring of spring constant 5 × 103 N/m is stretched initially by 5 cm from the unstretched position. Then the work required to stretch it further by another 5 cm is:
