Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Four equal charges of 2.0 × 10−6 C each are fixed at the four corners of a square of side 5 cm. Find the Coulomb's force experienced by one of the charges due to the other three.
उत्तर
Given,
Magnitude of the charges,
\[q = 2 \times {10}^{- 6} C\] Side of the square,
\[a = 5 \text{ cm = 0 . 05 m }\]
By Coulomb's Law, force,
\[F = \frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{q_1 q_2}{r^2}\]
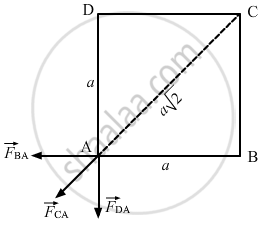
So, force on the charge at A due to the charge at B,
\[\vec{F}_{BA} = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times \left( 2 \times {10}^{- 6} \right)^2}{\left( 0 . 05 \right)^2} \]
\[ = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times 4 \times {10}^{- 12}}{25 \times {10}^{- 4}}\]
\[ = 14 . 4 N\]
Force on the charge at A due to the charge at C,
\[\vec{F}_{CA} = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times \left( 2 \times {10}^{- 6} \right)^2}{\left( \sqrt{2} \times 0 . 05 \right)^2}\]
\[ = \frac{9 \times {10}^9 \times 4 \times {10}^{- 12}}{25 \times 2 \times {10}^{- 4}}\]
\[ = 7 . 2 N\]
Force on the charge at A due to the charge at D,
\[\vec{F}_{DA} = \vec{F}_{BA}\]
The resultant force at A, F'= \[\vec{F}_{BA} + \vec{F}_{CA} + \vec{F}_{DA}\]
The resultant force of \[\vec{F}_{DA} \text{ and } \vec{F}_{BA}\] will be \[\sqrt{2} F_{BA}\] in the direction of \[\vec{F}_{CA}\] . Hence, the resultant force,
\[F' = 14 . 4\sqrt{2} + 7 . 2\]
\[ = 27 . 56 N\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check that the ratio ke2/G memp is dimensionless. Look up a Table of Physical Constants and determine the value of this ratio. What does the ratio signify?
Does the force on a charge due to another charge depend on the charges present nearby?
One end of a 10 cm long silk thread is fixed to a large vertical surface of a charged non-conducting plate and the other end is fastened to a small ball of mass 10 g and a charge of 4.0× 10-6 C. In equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical. Find the surface charge density on the plate.
Two insulating small spheres are rubbed against each other and placed 1 cm apart. If they attract each other with a force of 0.1 N, how many electrons were transferred from one sphere to the other during rubbing?
Ten positively-charged particles are kept fixed on the x-axis at points x = 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, ...., 100 cm. the first particle has a charge 1.0 × 10−8 C, the second 8 × 10−8 C, the third 27 × 10−8 C and so on. The tenth particle has a charge 1000 × 10−8 C. Find the magnitude of the electric force acting on a 1 C charge placed at the origin.
Two identical pith balls, each carrying a charge q, are suspended from a common point by two strings of equal length l. Find the mass of each ball if the angle between the strings is 2θ in equilibrium.
Two identically-charged particles are fastened to the two ends of a spring of spring constant 100 N m−1 and natural length 10 cm. The system rests on a smooth horizontal table. If the charge on each particle is 2.0 × 10−8 C, find the extension in the length of the spring. Assume that the extension is small as compared to the natural length. Justify this assumption after you solve the problem.
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C and a mass of 100 g is placed at the bottom of a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30°. Where should another particle B, with the same charge and mass, be placed on the incline so that it may remain in equilibrium?
Three identical charges, each with a value of 1.0 × 10−8 C, are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 20 cm. Find the electric field and potential at the centre of the triangle.
How much work has to be done in assembling three charged particles at the vertices of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure?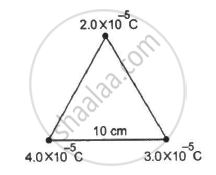
Answer the following question.
What is relative permittivity?
Solve numerical example.
Three equal charges of 10×10-8 C respectively, each located at the corners of a right triangle whose sides are 15 cm, 20 cm, and 25cm respectively. Find the force exerted on the charge located at the 90° angle.
Write down Coulomb’s law in vector form and mention what each term represents.
Write a short note on superposition principle.
Polarised dielectric is equivalent to ______.
The ratio of the forces between two small spheres with constant charge (a) in air (b) in a medium of dielectric constant K is ______.
The capacity of an isolate conducting sphere of radius R is proportional to
The S.I unit of electric permittivity is
Which of the following statements about nuclear forces is not true?
Two point charges +2 C and +6 C repel each other with a force of 12 N. If a charge of -4 C is given to each of these charges, then the force now is ______.
