Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A wire of length L and radius r is clamped rigidly at one end. When the other end of the wire is pulled by a force f, its length increases by l. Another wire of the same material of length 2L and radius 2r, is pulled by a force 2f. Find the increase in length of this wire.
उत्तर
Wire 1
L1 = L
f1 = r
A1 = πr2
F1 = f
ΔL1 = 1
Y1 = Y
Wire 2
L2 = 2L
f2 = 2r
A2 = π(2r)2 = 4πr2
F2 = 2f
ΔL2 = ?
Y2 = Y
As Y = `(FL)/(AΔL)` or ΔL = `(FL)/(AY)`
`(F_2L_2)/(A_2Y_2) = (F_2L_2)/(F_1L_1) xx (A_1Y_1)/(A_2Y_2) = (2f2L)/(fL) xx (pir^2 xx Y)/(4pir^2 xx Y)`
`(F_1L_1)/(A_1Y_1)`
`(ΔL_2)/1 = 4/4 = 1`
ΔL2 = 1
Thus, the change in the length of the second wire is also the same as that is one.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The dimension ML−1T−2 can correspond to
A vertical metal cylinder of radius 2 cm and length 2 m is fixed at the lower end and a load of 100 kg is put on it. Find (a) the stress (b) the strain and (c) the compression of the cylinder. Young modulus of the metal = 2 × 1011 N m−2.
The elastic limit of steel is 8 × 108 N m−2 and its Young modulus 2 × 1011 N m−2. Find the maximum elongation of a half-metre steel wire that can be given without exceeding the elastic limit.
A steel wire and a copper wire of equal length and equal cross-sectional area are joined end to end and the combination is subjected to a tension. Find the ratio of the stresses developed in the two wires .
The two wires shown in figure are made of the same material which has a breaking stress of 8 × 108 N m−2. The area of cross section of the upper wire is 0.006 cm2 and that of the lower wire is 0.003 cm2. The mass m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg and the hanger is light. Find the maximum load that can be put on the hanger without breaking a wire. Which wire will break first if the load is increased?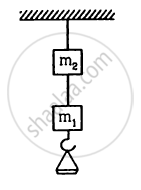
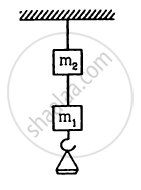
The two wires shown in figure are made of the same material which has a breaking stress of 8 × 108 N m−2. The area of cross section of the upper wire is 0.006 cm2 and that of the lower wire is 0.003 cm2. The mass m1 = 10 kg, m2 = 20 kg and the hanger is light. Repeat the above part if m1 = 10 kg and m2 = 36 kg.
Two persons pull a rope towards themselves. Each person exerts a force of 100 N on the rope. Find the Young modulus of the material of the rope if it extends in length by 1 cm. Original length of the rope = 2 m and the area of cross section = 2 cm2.
A sphere of mass 20 kg is suspended by a metal wire of unstretched length 4 m and diameter 1 mm. When in equilibrium, there is a clear gap of 2 mm between the sphere and the floor. The sphere is gently pushed aside so that the wire makes an angle θ with the vertical and is released. Find the maximum value of θ so that the sphere does not rub the floor. Young modulus of the metal of the wire is 2.0 × 1011 N m−2. Make appropriate approximations.
A steel wire of original length 1 m and cross-sectional area 4.00 mm2 is clamped at the two ends so that it lies horizontally and without tensions. If a load of 2.16 kg is suspended from the middle point of the wire, what would be its vertical depression ? Y of the steel = 2.0 × 1011 N m−2. Take g = 10 m s−2.
An equilateral triangle ABC is formed by two Cu rods AB and BC and one Al rod. It is heated in such a way that temperature of each rod increases by ∆T. Find change in the angle ABC. [Coeff. of linear expansion for Cu is α1, Coeff. of linear expansion for Al is α2]
