Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity of 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 Nm. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is ______.
पर्याय
7 μC
8 mC
2 mC
5 mC
उत्तर
An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30° with an electric field intensity of 2 × 105 N/C. It experiences a torque equal to 4 Nm. The charge on the dipole, if the dipole length is 2 cm, is 2 mC.
Explanation:
We know,
τ = pE.sinθ
∴ p = `tau/("E".sintheta)`
q × 2l = `4/(2 xx 10^5 xx 0.5)` ............(∵ p = q × 2l)
∴ q = `4/(2 xx 10^5 xx 0.5 xx 0.02)` ....(∵ 2l = 0.02m given)
= 2 × 10-3 C
q = 2 mC
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Depict the orientation of the dipole in (i) stable, (ii) unstable equilibrium in a uniform electric field.
An electric dipole is placed in an electric field generated by a point charge.
Two particles A and B, of opposite charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and −2.0 × 10−6 C, are placed at a separation of 1.0 cm. Calculate the electric field at a point on the axis of the dipole 1.0 cm away from the centre.
Two particles A and B, of opposite charges 2.0 × 10−6 C and −2.0 × 10−6 C, are placed at a separation of 1.0 cm. Calculate the electric field at a point on the perpendicular bisector of the dipole and 1.0 m away from the centre.
Answer the following question.
Derive an expression for the electric field at any point on the equatorial line of an electric dipole.
A conic surface is placed in a uniform electric field E as shown in the figure such that the field is perpendicular to the surface on the side AB. The base of the cone is of radius R, and the height of the cone is h. The angle of the cone is θ.
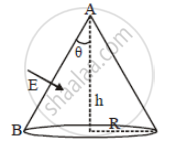
Find the magnitude of the flux that enters the cone's curved surface from the left side. Do not count the outgoing flux (θ < 45°)
The ratio of the weight of a man in a stationary lift and in a lift accelerating downwards with a uniform acceleration α is 3 : 2. The acceleration of the lift is:
The electric intensity due to a dipole of length 10 cm and having a charge of 500 µC, at a point on the axis at a distance 20 cm from one of the charges in air, is:
An electric dipole of moment `vec"p"` is placed normal to the lines of force of electric intensity `vec"E"`, then the work done in deflecting it through an angle of 180° is:
A dipole is placed in an electric field as shown. In which direction will it move?