Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following is NOT the property of equipotential surface?
पर्याय
They do not cross each other.
The rate of change of potential with distance on them is zero.
For a uniform electric field, they are concentric spheres.
They can be imaginary spheres.
The work done in carrying a charge from one point to another on an equipotential surface is zero.
उत्तर
For a uniform electric field, they are concentric spheres.
Explanation:
As all other statements are correct. In a uniform electric field, equipotential surfaces are never concentric spheres but are planes ⊥ to Electric field lines.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 µC at each of its vertices. Calculate the potential at the centre of the hexagon.
The top of the atmosphere is at about 400 kV with respect to the surface of the earth, corresponding to an electric field that decreases with altitude. Near the surface of the earth, the field is about 100 Vm−1. Why then do we not get an electric shock as we step out of our house into the open? (Assume the house to be a steel cage so there is no field inside!)
What is the geometrical shape of equipotential surfaces due to a single isolated charge?
Why is there no work done in moving a charge from one point to another on an equipotential surface?
Assertion: Electric field is discontinuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
Reason: Electric potential is continuous across the surface of a spherical charged shell.
Equipotential surfaces ______.
Equipotential surfaces ______.
- are closer in regions of large electric fields compared to regions of lower electric fields.
- will be more crowded near sharp edges of a conductor.
- will be more crowded near regions of large charge densities.
- will always be equally spaced.
The work done to move a charge along an equipotential from A to B ______.
- cannot be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- must be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- is zero.
- can have a non-zero value.
Find the equation of the equipotentials for an infinite cylinder of radius r0, carrying charge of linear density λ.
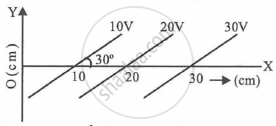
Equipotential surfaces are shown in figure. Then the electric field strength will be ______.