Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The work done to move a charge along an equipotential from A to B ______.
- cannot be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- must be defined as `- int_A^B E.dl`
- is zero.
- can have a non-zero value.
पर्याय
a and b
b and c
c and d
a and c
उत्तर
b and c
Explanation:
The work done by the external agent in shifting the test charge along the dashed line from 1 to 2 is
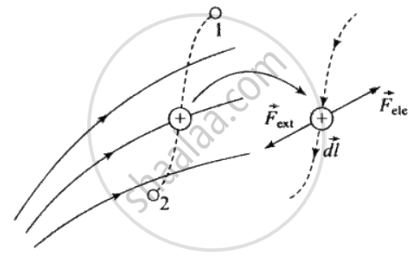
|
The external agent does a work `W = - q int_1^2 vecE * vec(dl)` in transporting the test charge q slowly from the positions 1 to 2 in the static electric field. |
`W_("ext") = int_1^2 vecF_("ext") * vec(dl) int_1^2 (-qvecE) * vec(dl) = - q int_1^2 vecE * vec(dl)`
We know `V_A - V_B = - int_A^B vecE * vec(dl)` ......(i)
`W_("electrical") = -ΔU = - qΔV = q(V_A - V_B)` ......(ii)
Hence from (i) and (ii), `W_("electrical") = q(V_A - V_B) = - qint_A^B vecE * vec(dl)`
If we want to calculate the work done to move a charge along an equipotential from A to B
For equipotential surface VA = VB, hence W = 0
Also electric field is perpendicular to equipotential surface, hence `vecE * vec(dl) => W_("electrical") = 0`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define an equipotential surface.
Draw a sketch of equipotential surfaces due to a single charge (-q), depicting the electric field lines due to the charge
Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to
(a) a constant electric field in the z-direction,
(b) a field that uniformly increases in magnitude but remains in a constant (say, z) direction,
(c) a single positive charge at the origin, and
(d) a uniform grid consisting of long equally spaced parallel charged wires in a plane.
What is the geometrical shape of equipotential surfaces due to a single isolated charge?
Answer the following question.
Two identical point charges, q each, are kept 2m apart in the air. A third point charge Q of unknown magnitude and sign is placed on the line joining the charges such that the system remains in equilibrium. Find the position and nature of Q.
Answer the following question.
Write two important characteristics of equipotential surfaces.
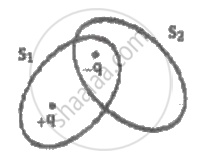
S1 and S2 are the two imaginary surfaces enclosing the charges +q and -q as shown. The electric flux through S1 and S2 are respectively ______.
- The potential at all the points on an equipotential surface is same.
- Equipotential surfaces never intersect each other.
- Work done in moving a charge from one point to other on an equipotential surface is zero.
Which of the following is NOT the property of equipotential surface?
Equipotential surfaces are shown in figure. Then the electric field strength will be ______.