Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current carrying long solenoid. Which of the following is true?
पर्याय
The electron will be accelerated along the axis.
The electron path will be circular about the axis.
The electron will experience a force at 45° to the axis and hence execute a helical path.
The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid.
उत्तर
The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity along the axis of the solenoid.
Explanation:
A solenoid consists of a helical winding of wire on a cylinder, usually circular in cross-section. There can be hundreds or thousands of closely spaced turns, each of which can be regarded as a circular loop. There may be several layers of windings.
Magnetic field due to solenoid B = μ0nl Direction of the field inside the solenoid is parallel to the axis, obtained by right-hand thumb rule as shown in figure.
F = q(v × B)
F = qvB*sinθ
Now, here an electron is moving in magnetic field of solenoid, so the concept of magnetic force comes into existence.
When an electron is projected with uniform velocity along the axis of a current carrying a long solenoid, then the magnetic force due to the magnetic field acting on the electron will be F = – evB sin 180° = 0 (either velocity is parallel to magnetic field or anti-parallel or 0 = 0° or 180° in both cases F = 0). The electron will continue to move with uniform velocity or will go undeflected along the axis of the solenoid.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A vertical wire carries a current in upward direction. An electron beam sent horizontally towards the wire will be deflected
Two parallel wires carry currents of 20 A and 40 A in opposite directions. Another wire carying a current anti parallel to 20 A is placed midway between the two wires. T he magnetic force on it will be
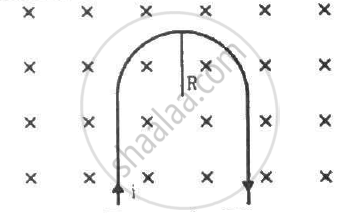
A rigid wire consists of a semi-circular portion of radius R and two straight sections (figure). The wire is partially immersed in a perpendicular magnetic field B, as shown in the figure. Find the magnetic force on the wire if it carries a current i.
Consider a straight piece of length x of a wire carrying a current i. Let P be a point on the perpendicular bisector of the piece, situated at a distance d from its middle point. Show that for d >> x, the magnetic field at P varies as 1/d2 whereas for d << x, it varies as 1/d.
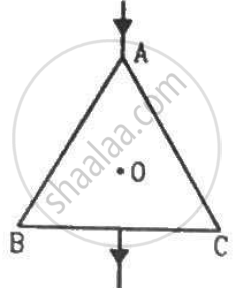
The wire ABC shown in figure forms an equilateral triangle. Find the magnetic field B at the centre O of the triangle assuming the wire to be uniform.
A straight horizontal conducting rod of length 0.45 m and mass 60 g is suspended by two vertical wires at its ends. A current of 5.0 A is set up in the rod through the wires.
(a) What magnetic field should be set up normal to the conductor in order that the tension in the wires is zero?
(b) What will be the total tension in the wires if the direction of current is reversed keeping the magnetic field same as before?
(Ignore the mass of the wires) g = 9.8 m s–2.
Correct expression for force on a current carrying conductor of length dl in a magnetic field is ______.
A charged particle is moving on circular path with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B, if the velocity of the charged particle is doubled and strength of magnetic field is halved, then radius becomes ______.
A straight conductor of length 2m moves at a speed of 20 m/s. When the conductor makes an angle of 30° with the direction of magnetic field of induction of 0.1 wbm2 then induced emf:
A conducting ring of radius 1m kept in a uniform magnetic field B of 0.01 T, rotates uniformly with an angular velocity 100 rad s−1 with its axis of rotation perpendicular to B. The maximum induced emf in it is:
