Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An em wave exerts pressure on the surface on which it is incident. Justify.
उत्तर
An em wave carries a linear momentum with it. The linear momentum carried by a portion of wave having energy U is given by `p=U/c`.Thus, if the wave incident on a material surface is completely absorbed, it delivers energy U and momentum `p=U/c` to the surface. If the wave is totally reflected, the momentum delivered is `p=(2U)/c` because the momentum of the wave changes from p to -p. Therefore, it follows that an em waves incident on a surface exert a force and hence a pressure on the surface.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
This is an example of step-up transformer.
State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic waves.
Why are e.m. waves non-mechanical?
Write a short note on the microwave.
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in free space along x-axis. At a particular point in space, the electric field along y-axis is 9.3 Vm−1. The magnetic induction (B) along z-axis is:
Dimensions of 1/(µOE0) is
The velocity of electromagnetic wave is parallel to
For a plane electromagnetic wave propagating in the x-direction, which one of the following combinations gives the correct possible directions for the electric field (E) and magnetic field (B) respectively?
An EM wave of intensity I falls on a surface kept in vacuum and exerts radiation pressure p on it. Which of the following are true?
- Radiation pressure is `I/c` if the wave is totally absorbed.
- Radiation pressure is `I/c` if the wave is totally reflected.
- Radiation pressure is `(2I)/c` if the wave is totally reflected.
- Radiation pressure is in the range `I/c < p < (2I)/c` for real surfaces.
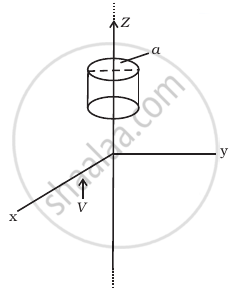
An infinitely long thin wire carrying a uniform linear static charge density λ is placed along the z-axis (figure). The wire is set into motion along its length with a uniform velocity `v = vhatk_z`. Calculate the poynting vector `S = 1/mu_0 (E xx B)`.