Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
पर्याय
1.1 p
p
less than p
between p and 1.1.
उत्तर
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be between p and 1.1.
Explanation:
According to the equation of ideal gas, PV = nRT
P = pressure
V = volume
n = Number of moles of gases
R = gas constant
T = temperature
Thus we have to rewrite this equation in such a way that no. of moles is given by,
`n = (PV)/(RT)`
The number of moles of the gas remain fixed, hence, we can write
`(P_1V_1)/(RT_1) = (P_2V_2)/(RT_2)`
⇒ `P_2 = (P_1V_1) (T/(V_2T_1))`
= `((P)(V)(1.1T))/((1.05)V(T))` .....`[(P_1 = P),(V_2 = 1.05 V and T_2 = 1.1T)]`
= `P xx ((1.1)/(1.05))`
= `P(1.0476) ≈ 1.05 P`
Hence, final pressure P2 lies between P and 1.1P.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
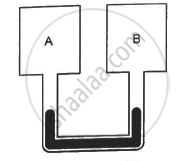
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
Energy is emitted from a hole in an electric furnace at the rate of 20 W when the temperature of the furnace is 727°C. What is the area of the hole? (Take Stefan’s constant σ to be 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.)
Compare the rates of emission of heat by a blackbody maintained at 727°C and at 227°C, if the black bodies are surrounded by an enclosure (black) at 27°C. What would be the ratio of their rates of loss of heat?
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
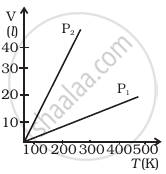
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
