Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
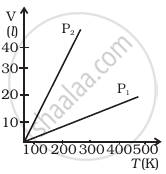
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
पर्याय
P1 > P2
P1 = P2
P1 < P2
data is insufficient.
उत्तर
P1 > P2
Explanation:
As we know that the pressure and the quantity of gas in the system are constants. Thus, by using the ideal gas equation
PV = nRT
V ∝ T .....(When n, P and R are constants)
`V_1/T_1` = constant
Or slope of graph is constant
`V = (nRT)/P`
`(dV)/(dT) = (nR)/P`
Or `(dV)/(dT)` increases when P decreases
Thus, `(dV)/(dT) ∝ 1/P`
This shows that slope P1 is smaller than P2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
Find the temperature of a blackbody if its spectrum has a peak at (a) λmax = 700 nm (visible), (b) λmax = 3 cm (microwave region) (c) λmax = 3 m (short radio waves). (Take Wien’s constant b = 2.897 × 10-3 m.K).
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
