Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following Figure shows a concave mirror MM' on which a ray of light incident from a point P gets reflected to meet the principle axis at O.
(a) Find, by construction, the position of the centre of curvature of the concave mirror.
(b) Write down the value for the radius of curvature of the mirror.
(c) Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
(d ) Which relation is used in deducing the focal length from the radius of curvature?
उत्तर
(i) Centre of curvature can be determined by constructing the imaginary sphere to which lens belongs.
(ii) Value of radius of curvature can be found by measuring the radius of this imaginary sphere geometrically.
(iii) The focal length is the midpoint of the pole and centre of curvature.
(iv) focal length of mirror = centre of curvature/2.
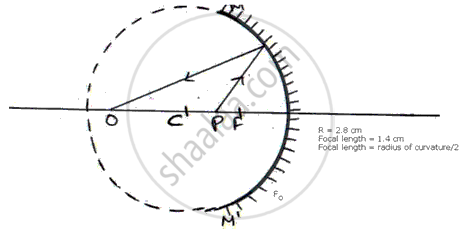 Centre of curvature = 2 .8 cm.
Centre of curvature = 2 .8 cm.
Focal length of mirror = 1.4 cm.
Focal length = radius of curvature/2.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane mirror. What will be the
angle of incidence?
A coin placed at the bottom of a vessel appears to be raised when water is poured in the vessel.
State the kind of mirror used
(a) by a dentist, and
(b) as a street light reflector.
AB and CD, two spherical mirrors, from parts of a hollow spherical ball with its centre at O as shown in the diagram. If arc AB = `1/2` arc CD, what is the ratio of their focal lengths? State which of the two mirrors will always form virtual image of an object placed in front of it and why.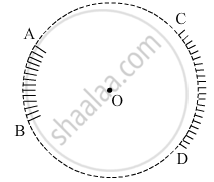
Name the mirror which always produces an erect and virtual image. How is the size of image related to the size of object?
Why does a driver use a convex mirror instead of a plane mirror as a rear view mirror?
Illustrate your answer with the help of a ray diagram.
A point light source is kept in front of a convex mirror at a distance of 40 cm. The focal length of the mirror is 40 cm. Find the position of image.
Define the following term in relation to concave mirror.
Principal focus
