Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object is placed 15 cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
उत्तर
`m=(-6)/-15`
m=0.4
Thus, the image is virtual, erect and small in size.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
A concave mirror has a focal length of 25 cm. At which of the following distance should a person hold his face from this concave mirror so that it may act as a shaving mirror?
(a) 45 cm
(b) 20 cm
(c) 25 cm
(d) 30 cm
Give reason for your choice.
According to the "New Cartesian Singh Convention" for mirrors, what sign has been given to the focal length of:
a concave mirror?
A converging mirror forms a real image of height 4 cm of an object of height 1 cm placed 20 cm away from the mirror:
- Calculate the image distance.
- What is the focal length of the mirror?
Why does a beam of light when it enters glass at an angle? Why does it not bend if it inters the glass at right angles?
State two uses of a concave mirror.
A student has focused the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a concave mirror. The situation is as given below:
Length of the flame = 1.5 cm
Distance of flame from the mirror = 18 cm
If the flame is perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror, then calculate the following:
- Distance of the image from the mirror
- Length of the image
If the distance between the mirror and the flame is reduced to 10 cm, then what would be observed on the screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer for this situation.
Why does obtaining the image of the sun on paper with the help of a concave mirror burn the paper?
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
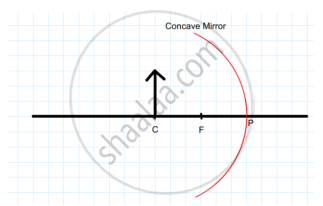
Examine the above figure and state which of the following option is correct? [one small box in the figure is equal to 1 cm]
