Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An object is placed 15 cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20 cm. Calculate the image position and magnification in each case.
Solution
m=0.4
Thus, the image is virtual, erect and small in size.
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object of height 5 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. If the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 20 cm, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed using the lens formula.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of light which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm.
If an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
An object is 100 mm in front of a concave mirror which produces an upright (erect image). The radius of curvature of the mirror is ______.
A real image of an object is to be obtained. The mirror required for this purpose is:
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) either convex or concave
A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of object. For the virtual position of object, the position of object will be at ______.
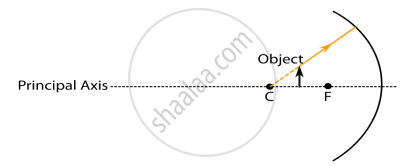
While looking at the above diagram, Nalini concluded the following.
- the image of the object will be a virtual one.
- the reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
- the image of the object will be inverted.
- this is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
An image formed by a lens is erect. Such an image could be formed by a
