Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litres has an initial gauge pressure of 15 atm and a temperature of 27 °C. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, the gauge pressure drops to 11 atm and its temperature drops to 17 °C. Estimate the mass of oxygen taken out of the cylinder (R = 8.31 J mol–1 K–1, molecular mass of O2 = 32 u)
उत्तर १
Volume of oxygen, V1 = 30 litres = 30 × 10–3 m3
Gauge pressure, P1 = 15 atm = 15 × 1.013 × 105 Pa
Temperature, T1 = 27°C = 300 K
Universal gas constant, R = 8.314 J mole–1 K–1
Let the initial number of moles of oxygen gas in the cylinder be n1.
The gas equation is given as:
`P_1V_1 = eta_1RT_1`
`:.n_1 = P_1V_1/RT_1`
`= (15.195 xx10^5 xx 30 xx 10^(-3))/((8.314) xx 300) = 18.276`
Where,
m1 = Initial mass of oxygen
M = Molecular mass of oxygen = 32 g
∴m1 = n1M = 18.276 × 32 = 584.84 g
After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, the pressure and temperature reduces.
Volume, V2 = 30 litres = 30 × 10–3 m3
Gauge pressure, P2 = 11 atm = 11 × 1.013 × 105 Pa
Temperature, T2 = 17°C = 290 K
Let n2 be the number of moles of oxygen left in the cylinder.
The gas equation is given as:
P2V2 = n2RT2
`:. n_2= (P_2V_2)/(RT_2)`
`= (11.143 xx 10^5 xx 30 xx 10^(-3))/8.314 xx 290 = 13.86`
But `n_2 = m_2/M`
Where,
m2 is the mass of oxygen remaining in the cylinder
∴m2 = n2M = 13.86 × 32 = 453.1 g
The mass of oxygen taken out of the cylinder is given by the relation:
Initial mass of oxygen in the cylinder – Final mass of oxygen in the cylinder
= m1 – m2
= 584.84 g – 453.1 g
= 131.74 g
= 0.131 kg
Therefore, 0.131 kg of oxygen is taken out of the cylinder.
उत्तर २
Initial Volume, `V_1 = 30 litre = 30 xx 10^3 cm^3`
`= 30 xx 10^3 xx 10^(-6) m^3 = 30 xx 10^(-3) m^3`
Initla Pressure, P_1 = 15 atm
`= 15 xx1.013 xx 10^5 N m^(-2)`
Inital temperature, `T_1 = (27 + 273) K = 300 K`
Initial number of moles
`mu_1 = (P_1V_1)/RT_1 = (15xx1.013 xx10^5 xx 30xx10^(-3))/(8.31 xx 300) = 18.3`
Final Pressure, `P_2 = 11 atm`
`= 11 xx 1.013 xx 10^5 N m^(-2)`
Final Volume, V`_2 = 30 litre = 30 xx 10^(-3) cm^3`
Final temperature, `T_2 = 17 + 273 = 290 K`
Final number of moless, `mu_2 = (P_2V_2)/(RT_2) = (11xx 1.013xx 10^5xx 30xx10^(-3))/(8.31 xx 290) = 13.9`
Number of moles takesout of cyclinder = 18.3 - 13.9 = 4.4
Mass of gas taken out of cylinder = 4.4 xx 32 g = 140.8 g = 0.141 kg
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The figure shows the plot of PV/T versus Pfor 1.00×10–3 kg of oxygen gas at two different temperatures.
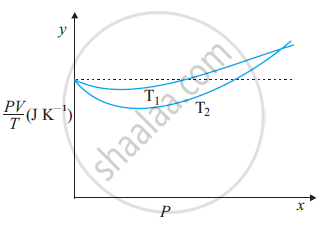
(a) What does the dotted plot signify?
(b) Which is true: T1 > T2 or T1 < T2?
(c) What is the value of PV/T where the curves meet on the y-axis?
(d) If we obtained similar plots for 1.00 ×10–3 kg of hydrogen, would we get the same value of PV/T at the point where the curves meet on the y-axis? If not, what mass of hydrogen yields the same value of PV/T (for low pressure high temperature region of the plot)? (Molecular mass of H2 = 2.02 u, of O2 = 32.0 u, R = 8.31 J mo1–1 K–1.)
Oxygen is filled in a closed metal jar of volume 1.0 × 10−3 m3 at a pressure of 1.5 × 105Pa and temperature 400 K. The jar has a small leak in it. The atmospheric pressure is 1.0 × 105 Pa and the atmospheric temperature is 300 K. Find the mass of the gas that leaks out by the time the pressure and the temperature inside the jar equalise with the surrounding.
Give reasons for the following:
Gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept.
Fill in the blanks:
If the temperature is reduced to half, ………….. would also reduce to half.
A gas occupies 500 cm3 at a normal temperature. At what temperature will the volume of the gas be reduced by 20% of its original volume, the pressure is constant?
Name or state the following:
An equation used in chemical calculations which gives a simultaneous effect of changes of temperature and pressure on the volume of a given mass of dry gas
The average energy per molecule is proportional to ______
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Do the vessels contain an equal number of respective molecules?
Calculate the number of atoms in 39.4 g gold. Molar mass of gold is 197g mole–1.
Cooking gas containers are kept in a lorry moving with uniform speed. The temperature of the gas molecules inside will ______.
